From Hydro by Ian Russell (article in PDF)
What You See is Not Always What You Get
When ships run aground unexpectedly the initial presumption is that the vessel has struck an ‘uncharted’ feature.
In practice this is rarely so.
This article reviews a number of chart-related casualties.
These demonstrate that while no charts are infallible, a better appreciation of their limitations might have averted disaster.
New cruise ship itineraries in tropical seas and Polar Regions require especial vigilance.
Ever deeper draught bulk cargo and crude carriers are transiting sparsely surveyed ocean areas and accessing remote locations in the continuing search for and exploitation of new mineral deposits.
Are these accidents waiting to happen?
Today’s navigators often
venture where available hydrographic data does not meet the requirements of contemporary shipping.
Member States of the
International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) acknowledge this deficiency and are pledged to remedy it; but this will take time.
The circumstances leading to past mishaps are therefore potentially present both now and in future. Although the charts in use in some of the cited casualties were compiled from lead-line surveys; they provided ample evidence that less water than charted might be expected.
Accounts of accidents often reveal the vessel’s speed to have been excessive in the circumstances.
The IHO defines inadequately surveyed areas as those where bathymetry is based on older lead-line surveys or other surveys which are either open in nature or not hydrographic surveys.
International Maritime Organisation (IMO) Guidelines on Voyage Planning for Passenger Ships Operating in Remote Areas, adopted in 2007, indicate that planning should take into account the source, date and quality of the hydrographic data of charts used.
Navigators should remember that the nearest point of land is almost always the seabed, as the case studies demonstrate.
Case 1 (Caribbean Calamity)
In January 1971, the former French
passenger liner Antilles (length over all (l.o.a.) 183m, beam 24.4m, draught 8m) struck an uncharted reef off the NW coast of Mustique in the Grenadine Islands. As the ship was proceeding at 16 knots the impact caused her to break in two and catch fire.
The passage being attempted was through apparently open water some 640m wide, with charted depths of 13 and 16 metres.
It lay between two rock outcrops, in a coral and reef-strewn area last surveyed in the 19th century.
This followed a change to the planned route; authorized by the master in order, as the subsequent legal proceedings revealed, ‘to provide his passengers with a better look at this enchanting isle and was consistent with his desire to implement the Owner’s policy of making Antilles’ cruises entertaining and unique’.
Case 2 (Déja vu)
In April 2000, the ‘Adventure’ cruise ship World Discoverer (l.o.a. 87m, beam 15m, draught 4.57m) grounded on an allegedly uncharted feature in Sandfly Passage, Solomon Islands.
Image courtesy: Philjones828, via Wikimedia Commons.
The ship was fatally holed and the master beached her in Roderick Dhu Bay, where the hulk remains.
Sandfly passage and Roderick Dhu Bay (NGA chart #82377)
with the Marine GeoGarage
Neither the Australian Hydrographic Service nor the UK Hydrographic Office, the Primary Charting Authority, has any record of the incident.
The stranded wreck of World Discoverer is clearly visible on Google Earth,
but is not shown on the latest (2012) edition of chart BA 1713.
(GeoGarage note : scale too low)
Figure 1a: Portion of Chart BA1713.
Image courtesy: Crown Copyright and/or database rights.
The Pacific Island Pilot, current at the date of the incident, advises that “Deep-draught vessels should not attempt the passage owing to the reefs in the N entrance.”
The latest (2007) edition of the Pilot directs vessels west of Mid Reef; passing clear of the 9.1m patch.
This remains the least depth shown in the passage other than the reef itself.
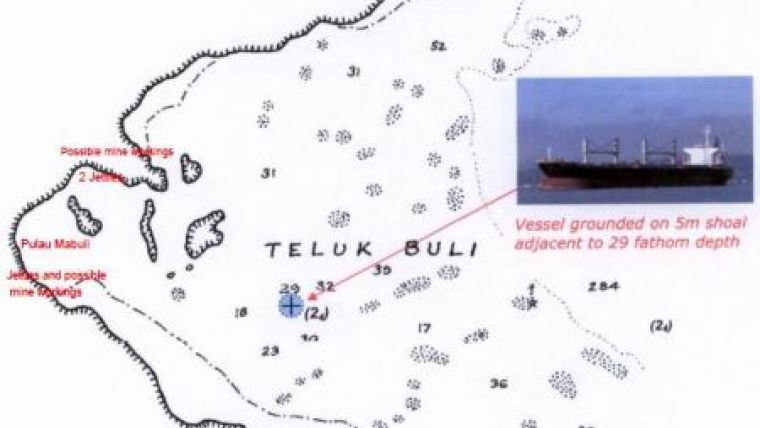
Case 3 (Uncharted but not Unexpected)
Such dangers also exist for large cargo vessels navigating in poorly charted waters.
In 2010, the bulk carrier Noble Hawk (l.o.a.190m, beam 33m, draught 12.5m), outbound from Teluk Buli in Eastern Indonesia to China, grounded on an uncharted 5m shoal.
Surrounding depths were 53 to 58m.
Her course lay across a large bay encumbered with islets, reefs and shoals.
Figure 2: Sketch map derived from Chart BA 2788 (Halmahera and the Adjacent Islands),
compiled from 20th
century lead-line surveys, showing position of grounding in relation to
Noble Hawk’s departure point, adjacent depths and shoal areas.
The chart in use was compiled from 20th century lead-line surveys.
In 2012, the
Indonesian Navy Hydrographic Service (DISHIDROS) carried out a survey of the grounding site and found a least depth of 3m and an adjacent depth of 15.3m in general depths of 50m.
Mindful of the significant activity of large cruise ships and bulk carriers in these waters DISHIDROS recommended that the new shoal be marked.
Case 4 (Ennerdale Rocks)
In 1970, a Royal Fleet Auxiliary vessel the tanker Ennerdale (l.o.a. 227m, beam 30m, draught 12m) struck a rock pinnacle about 8 miles NNE of Port Victoria in the Seychelles and sank.
1 June 1970 whilst outbound from Port Victoria, Mahe in the Seychelles Islands to refuel the frigate HMS ANDROMEDA she struck an uncharted pinnacle of rock in position 04.30 N 055.31 E which opened up her starboard side and she heeled over very quickly and settled on the bottom with her stern section submerged and her bow in the air fortunately without any loss of life
The pinnacle, which was charted at 9 fms (16.5m), lay adjacent to a 10 fm (18.3m) sounding in general depths of 13 to16 fms (23.8 to 29.3m).
The vessel, travelling at 12kts, was crossing a line of pinnacles and islet outcrops which extend north-eastwards from the north tip of the Island of Mahé within the 20 fathom line.
The chart in use was compiled from a 19th century lead-line survey, as stated in the title.
The least depth of water over the pinnacle (subsequently established at 10.8m (35ft)) was not shown on this chart.
However, there was sufficient indication on the chart that shoaler water may well have existed in the vicinity.
Ennerdale rocks with the Marine GeoGarage (British Admiralty chart)
Figure 3: Portion of Chart BA
1072, current at the time of the grounding, showing the 9 fathom shoal
patch on which the vessel struck and the adjacent 10 fathom patch.
Image courtesy: Crown Copyright and/or database rights.
Reproduced by permission of the Controller of Her Majesty’s Stationery Office
and the UK Hydrographic Office
The previously unnamed feature is now charted as Ennerdale Rocks.
Cases 5 & 6 (Dangers of the Deep)
In 1973, the cargo ship Muirfield, drawing 16m, was on passage from the Cape of Good Hope to Selat Sunda.
There was a 2-3m swell running when she struck the top of a
seamount, 75 miles south west of the Cocos Islands.
A subsequent survey found a shoal with a least depth of 18m in charted depths of over 5,000m.
Submarine Surprised
More than 90% of all seamounts greater than 1km in height (estimated to be more than 100,000) are unobserved by either ship soundings or satellite gravity (Sandwell & Wessel, 2010).
This observation is consistent with the statement in
IHO publication C-55 that renewed attention needs to be given to the disproving of vigias especially adjacent to the maritime shipping routes in the Pacific and adjacent seas.
The danger to submarine navigation is self evident.
In 2005
USS San Francisco, a nuclear powered submarine, collided with a seamount about 364 nautical miles southeast of Guam.
(see NYTimes)
San Francisco dry-docked at Guam on January 27,2005
The submarine was travelling at maximum speed at a depth of 160m.
The seamount that she struck did not appear on the chart in use at the time of the accident.
Other charts available showed an area of ‘discoloured water’, an indication of the probable presence of a seamount.
Subsequent investigation determined that information regarding the seamount should have been transferred to the charts in use, particularly given the relatively uncharted nature of the ocean area that was being transited.
(source : navy.mil)
Discussion
Figure 3 The progressive increase in the size of vessels.
The dimensions of those now at sea and on order,
reflect the shipping industry’s response to changing operational and trading patterns.
Despite a steady increase in the length of cruise ships the draught of the current vessels in service has not increased proportionately and averages 8.4m.
However, these ships are venturing into increasingly remote and poorly charted areas. Itineraries that seek to provide optimum passenger experience are potentially hazardous.
Many of the smaller vessels (l.o.a. <100m) that offer adventure cruises are fitted with forward looking sonar and can deploy portable echo sounders in their tenders.
The report of an investigation into the incident in the Canadian Artic highlights the necessity for such provision.
The significant draughts in Figure 3 are those of the large cargo vessels.
New Panamax vessels transiting the Caribbean may not be able to do so with the same confidence as their predecessors.
Elsewhere ULCC and large bulk carriers are vulnerable to an encounter with an uncharted seamount rising close to the surface.
In the deep areas of the ocean, most mariners consider that there is little chance of a vessel running aground on such a feature.
Unfortunately, this is a misconception.
Examples of navigationally significant seamounts include
Vema Seamount (with a charted depth of 11 metres - about 1,000km west-north-west of Cape Town)
and Walters Shoal Seamount (with a charted depth of 15 metres - about 400 nautical miles south of Madagascar).
These seamounts rise up from ocean depths of about 4,000 and 2,000 metres respectively.
(see AWI last seamounts discoveries, June 2014)
Conclusions
Australia has the third largest ocean territory in the world, but we've only mapped 12 per cent of it. The RV Investigator is using state of the art equipment and design to map the sea floor.
Many locations being accessed by cruise ships and deeper draught cargo vessels are unlikely to be surveyed to full modern standards in the foreseeable future.
Navigators of these vessels therefore need to ensure that they fully appreciate the limitations of available hydrographic data and act accordingly.
More owners should perhaps consider installing forward looking sonars for vessels operating in Polar Regions and away from recognised routes elsewhere.
Such action might well have saved World Discoverer.
It should also have prevented the damage to Noble Hawk, which incurred significant salvage and repair costs as well as the associated loss of revenue”.
Links :