Government funds prop up more than half of fishing in the open ocean, a new study reveal
A fish’s journey from ocean to plate may not be as straightforward as it sounds.
Most people are aware that a fisher, a grocer and a cook were involved in that journey.
But a new study finds that governments lend a hand, too—and a mighty big one.
A paper, published Wednesday in the journal Science Advances, found that as much as 54 percent of high seas fishing would be unprofitable were it not for governments covering some of the industry's costs.
To a lesser degree, the study also found that exploited labor and underreported catch may explain how large vessels afford to fish in international waters.
“The study confirmed that much of the high seas fishing does not make sense,” says study author and National Geographic Explorer-in-Residence Enric Sala.
“If it's ecologically destructive and economically unprofitable, why don't we end all high seas fishing?”
A fisherman checks his fishing lines while fishing on the high seas.
The
high seas is defined as the open waters outside a country's exclusive
economic zone, generally 200 miles past the shore.
Photograph by Chris Johns, National Geographic Creative
In 2016, just over 3,600 vessels actively fished on the high seas—the open ocean outside any country's jurisdiction.
To better understand this impact, the research team of ecologists, data scientists, and economists looked at the most recent cost datasets available, from 2014.
They found that the total cost of fishing in that year ranged anywhere from 6.2 to 8 billion USD and that subsidies totaled around 4.2 billion USD.
This boat is fishing for tuna, a species commonly fished out of the high seas.
Photograph by Paul Nicklen, National Geographic Creative
By far, their data showed that China and Taiwan net the fewest profits in the sector, while exerting some of the most effort.
Russia was also shown to have an unprofitable fishing industry, even with subsidies.
However, subsidies weren't just given to unprofitable fishing vessels.
The study also found that marginally profitable companies in Japan, South Korea, Spain, and the U.S.
had their profits boosted by government subsidies.
“There are three different categories [of subsidies],” says University of British Columbia economist Rashid Sumaila, one of the study's authors.
He and his colleagues began compiling data on fishing subsidies in 2000, and they found that not all subsidies were harmful.
Some were ambiguous and hard to categorize.
Others were beneficial and went toward activities like sustainable management, research, and regulation enforcement.
Other subsidies helped companies increase their carrying capacity—essentially these allowed boats to fish more in fisheries that might be at risk of depletion.
Rather than directly providing a fishing company with a check, governments may offer tax breaks, help pay for fuel costs, provide money to upgrade gear, or fund infrastructure like ports.
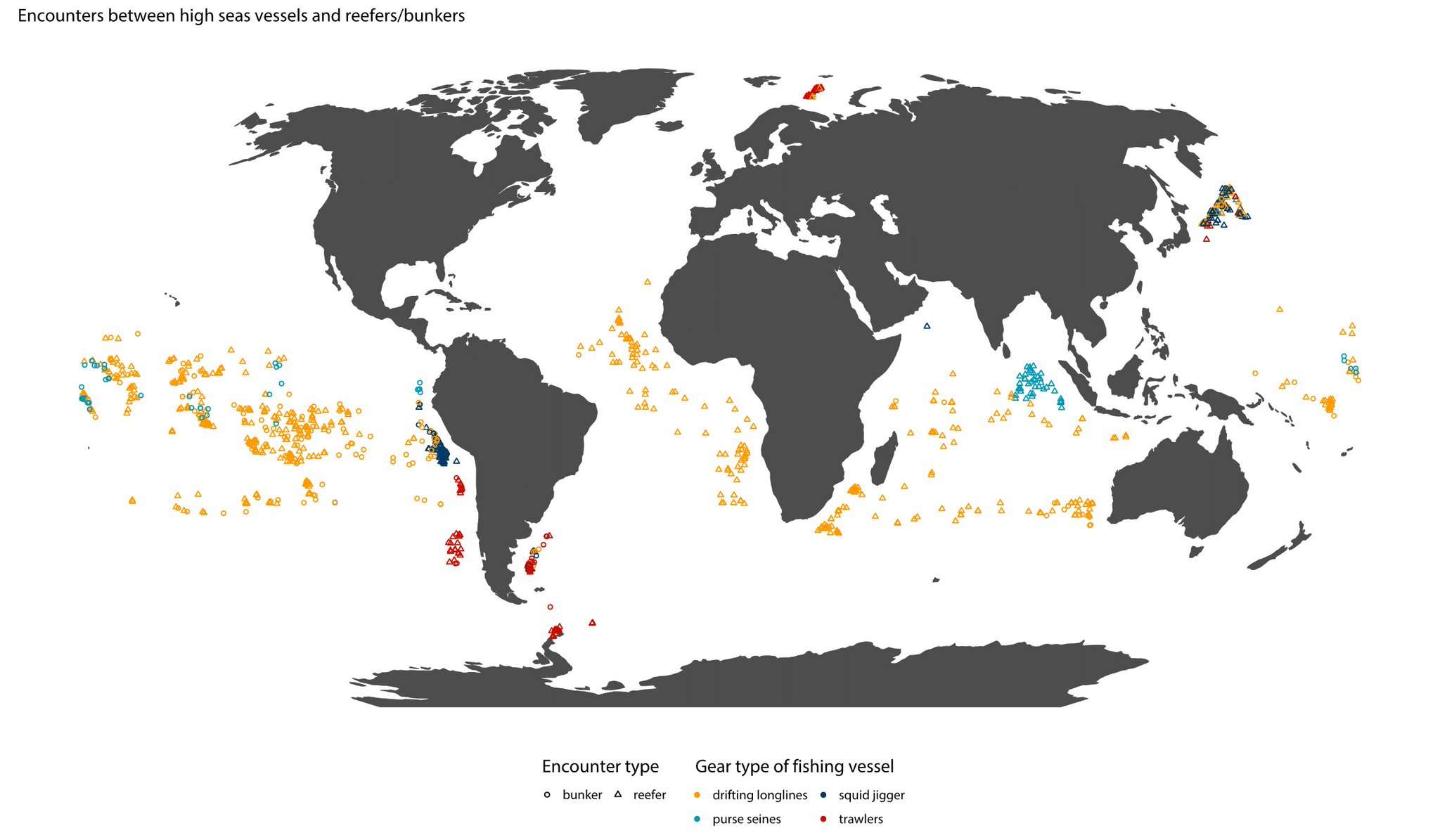
Encounters between high seas vessels and reefers/bunkers
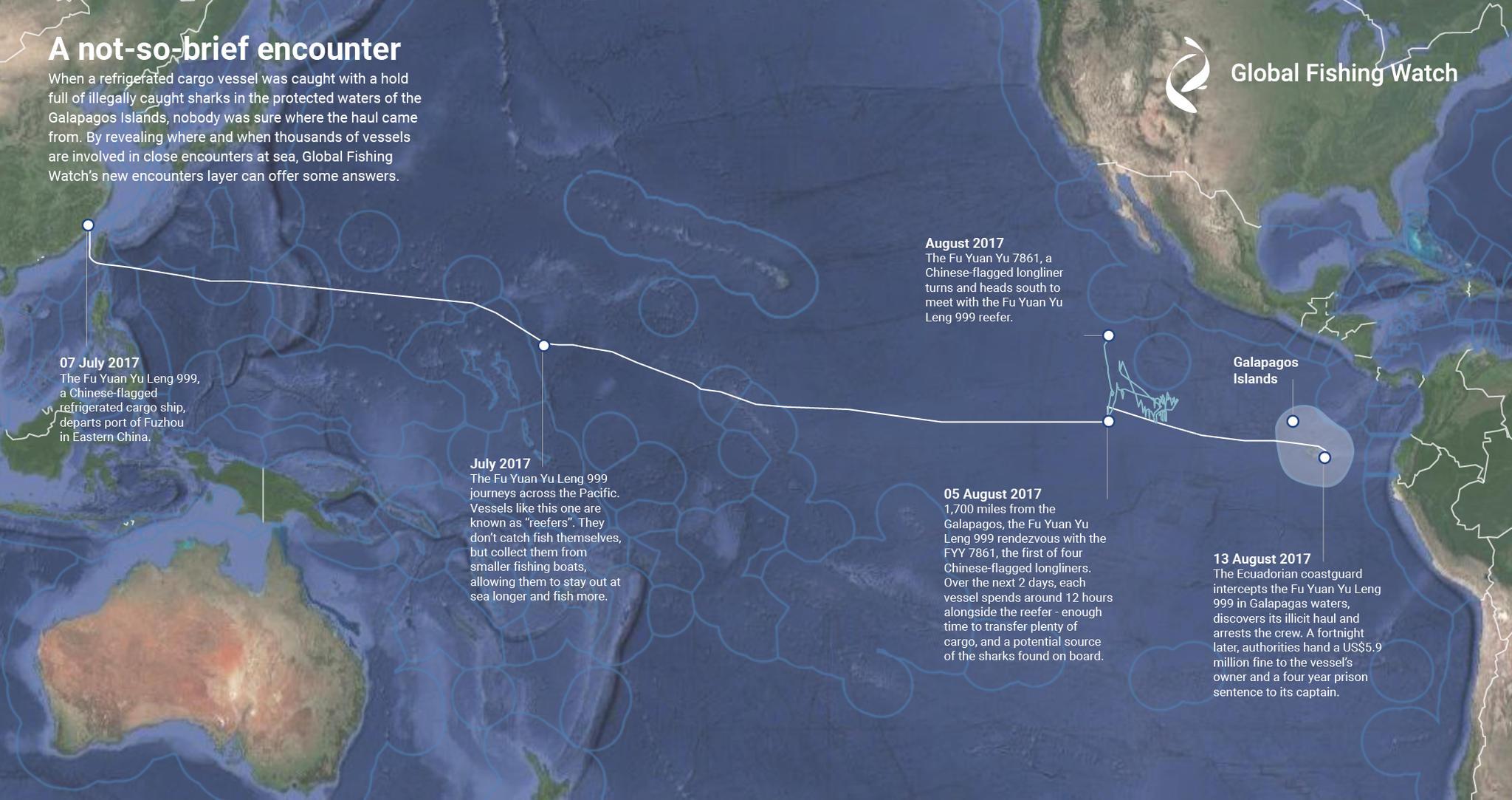
Spying from space
Open ocean outside EEZs, generally 200 miles beyond the shore, is free game.
The UN's Food and Agriculture Organization outlines a code of conduct on these high seas, but regulation is minimal and enforcement is scant.
What's more, vessels often have a competitive interest in not sharing details about their activities.
Global Fishing Watch's new encounters layer reveals for the first time where and when thousands of vessels are involved in close encounters at sea.
To detect pairs of vessels meeting at sea, analysts applied machine learning algorithms to more than 30 billion Automatic Identification System (AIS) messages from ocean-going boats to find tell-tale transshipment behaviour, such as two vessels alongside each other long enough to transfer catch, crew, or supplies.
To detect pairs of vessels meeting at sea, analysts applied machine learning algorithms to more than 30 billion Automatic Identification System (AIS) messages from ocean-going boats to find tell-tale transshipment behaviour, such as two vessels alongside each other long enough to transfer catch, crew, or supplies.
To compile data for one of the world's most inaccessible regions, marine data scientist and study author Juan Mayorga turned to a program called Global Fishing Watch that tracks vessels from space using the satellite-transmitted signal from AIS—Automatic Identification System—that vessels are required to transmit.
Earlier this year, he used the data to find that industrial fishing covers a third of the planet.
“When we first came up with this idea, we did not have a good handle on what fishing on the high seas looked like,” says Mayorga.
Over a two-year period, he determined how many vessels were operating in the high seas and how often, though he adds that the study's data can't account for all high seas fishing activity.
Some vessels forego AIS or turn it off to intentionally be covert.
With the data for the ships they could measure, Mayorga used models to estimate fuel costs based on a vessel's size, location, distance traveled, and speed.
He could also see the type of vessel and what it was fishing for, which helped him estimate needed labor.
Looking at existing information on minimum wage laws and typical cost of labor, Mayorga was able to estimate labor costs on a scale.
He notes, however, that this estimate is the least certain part of the study, because reports from several non-governmental organizations show the fishing industry has a history of exploitative labor practices, verging on or directly resulting in slave labor in some regions.
“Labor is what drives the uncertainty in our analyses,” he says.
With his range of operating costs, Mayorga then estimated the haul each vessel was bringing to market.
The study's authors suspect that catch may be underreported in some cases.
Bottom trawling is one of the most destructive fishing practices.
It
commonly drags coral from the ocean floor, like this large piece of
Paragorgia coral dredged from waters near New Zealand.
Impacts
All-in-all, industrial fishing on the high seas is a relatively small portion of global fishing—accounting for only six percent of all fishing activity.
Fishing subsidies in EEZs have been controversial, with the World Trade Organization considering banning them in the past decade.
So why subsidize fishing for more expensive fleets that yield smaller returns, the study's authors ask.
According to a representative from the UN's Food and Agriculture Organization, food security is often cited as a major reason for providing subsidies to fishing industries.
But a statement published by the agency in 2016 acknowledges a need to regulate subsidies to ensure sustainability.
“Fisheries subsidies warrant concern,” says FAO representative Christopher Emsden, adding, “Care is needed as they can serve development purposes in some cases, (although these would likely be for small-scale fishers and not those featuring in the study).”
The study identified squid fishing as an unsustainable but government-funded fishing practice.This fisherman holds a squid in the green light they use to bait them.
Photograph by Ben Horton, National Geographic Creative
Photograph by Ben Horton, National Geographic Creative
In addition to depleting fisheries, high seas fishing subsidies also threaten important natural habitats, says Sala.
Deep-sea bottom trawling, one of more common high-seas fishing practices, is problematic, he notes.
“Trawling is one of the most destructive practices on the planet,” says Sala.
“They have nets so large they can hold a dozen 747 jets.
These huge nets destroy everything in their path, including deep-sea corals.
And it would not be profitable without subsidies.”
In addition, all three researchers noted that high-seas fishing may perpetuate exploitation.
“[Unprofitability] has implications about the extent to which unfair labor practices drive fishing on the high seas,” notes Mayorga.
What if we could save the fishing industry and protect the ocean at the
same time?
Marine ecologist Enric Sala shares his bold plan to safeguard
the high seas -- some of the last wild places on earth, which fall
outside the jurisdiction of any single country -- by creating a giant
marine reserve that covers two-thirds of the world's ocean.
By
protecting the high seas, Sala believes we will restore the ecological,
economic and social benefits of the ocean.
"When we can align economic
needs with conservation, miracles can happen," Sala says.
The future of high-seas fishing
Transparency, whether because industry officials intentionally withheld information or governments lacked records, presented a major hurdle for how researchers comprehensively assessed the high-seas fishing industry.
To combat what they say is an economically and environmentally unsound practice, the research team says increasing transparency is key.
More stringently enforcing AIS, for example, is one way Sala says regulators could monitor the full impact of high-seas fishing.
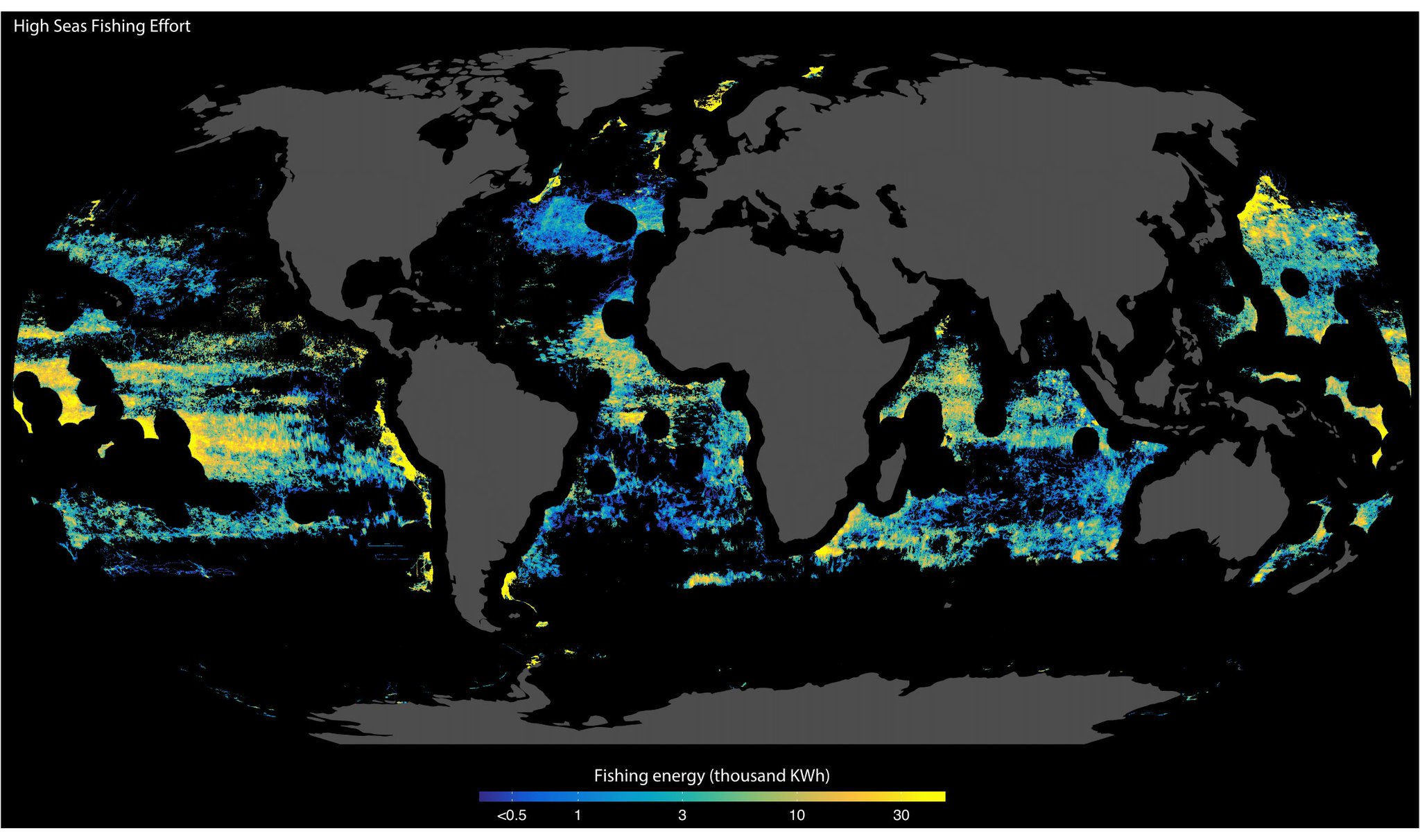
High seas fishing effort (energy in kWh)
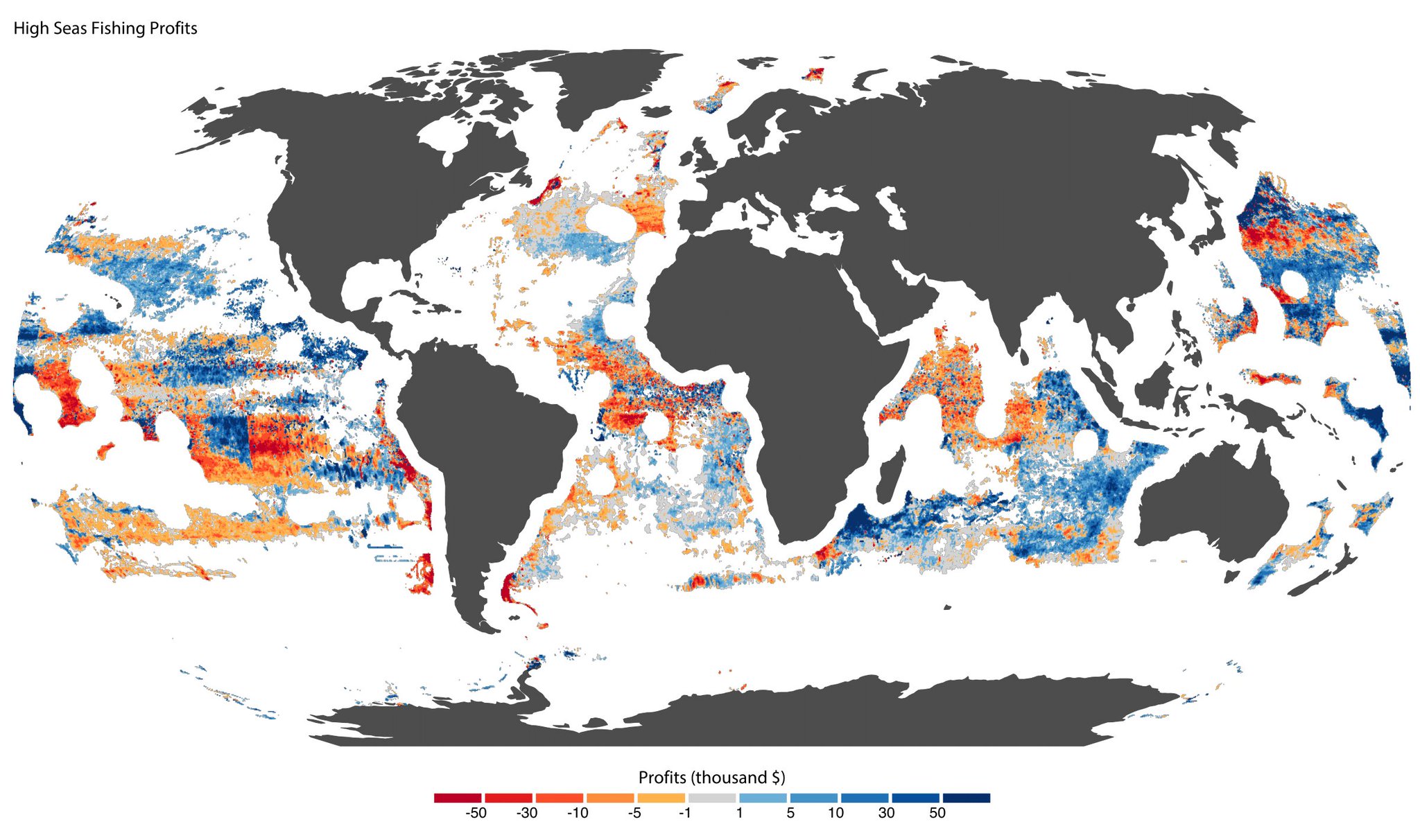
High seas fishing profits in thousands US$
courtesy of Global Fishing Watch
courtesy of Global Fishing Watch
Sumaila would like to see the World Trade Organization ban or roll back fishing subsidies, but despite extensive discussion at the organization progress has been minimal.
The last vote was shot down in December of last year, primarily due to procedural hurdles.
The WTO will consider changes to fishing subsidies again in 2019.
The high seas have sometimes been seen as an avenue for countries to compensate for other overfished waters.
China, for instance, has experienced extensive overfishing in its own waters, and a study published in April 2017 found the country trying to compensate by fishing in waters as far as western Africa.
Depleting fisheries is a growing problem.
Of the 600 fisheries monitored by the FAO, more than half are depleted to the point of yielding little to no catch.
Last December, the U.N. also began talks to create a framework to protect high-seas biodiversity.
Negotiations are expected to be ongoing for the next two years.
The high seas doesn't belong to any one country, which means regional governments often clash during negotiations.
In the past, some have objected to long-term changes, hoping to leave the door open to commercial opportunity, while others are worried they may be impacted by declining biodiversity.
Links :
- Sciences Advances : The economics of fishing the high seas
- Phys : Study on economics of fishing on the high seas
- Earth : High seas fishing is unprofitable without government subsidies
- Nature : How to save the high seas
- Pew : What Do You Know About Illegal Fishing?
- Pacific Standard : This Satellite-Based Monitoring System Could Be a Game-Changer for ...
- BBC : How to spot the secretive activities of rogue fishing boats
- Reuters Graphics : Casting a wider net, how fishing fleets comb the ocean
- GeoGarage blog : New maps show the utterly massive imprint of fishing on the world's ... / The way the world catches fish defies all economic ... / How illegal fishing is being tracked from space / Nine of world's biggest fishing firms sign up to ... / Fighting illegal fishing with Big Data / Big brother at sea / An ingenious use of big data helped expose a ... / Global Fishing Watch lets you track 35000 fishing ... / Google's global fishing watch is using 'manipulated ... / How satellite technology is helping to fight illegal fishing / The plan to map illegal fishing from Space





No comments:
Post a Comment