 The
wreck lies about 1,600 feet from the shore, at a depth of about 20
feet;
The
wreck lies about 1,600 feet from the shore, at a depth of about 20
feet; it may be developed as an underwater museum for divers.
(Image
credit: Filipe Castro)
From LiveScience By Tom Metcalfe
Researchers think the wreck was part of a flotilla that accompanied the Portuguese explorer's final voyage.
A wreck off the coast of Kenya may have been a ship from one of Vasco da Gama's pioneering voyages into the Indian Ocean 500 years ago, archaeologists say.
The remains of the vessel, which were discovered near the Kenyan town of Malindi in 2013, are among eight known Portuguese shipwrecks from this period in the area.
Malindi nautical chart (NGA) in the GeoGarage platform
Researchers think it may be the São Jorge, which sank in 1524, although the identification is not certain.
If the wreck is the São Jorge, it would make it the earliest European shipwreck in the Indian Ocean, but "we don't know for sure," Filipe Castro, a maritime archaeologist at the University of Coimbra in Portugal and lead author of a new study describing the recent work, told Live Science.
If the wreck is the São Jorge, it would make it the earliest European shipwreck in the Indian Ocean, but "we don't know for sure," Filipe Castro, a maritime archaeologist at the University of Coimbra in Portugal and lead author of a new study describing the recent work, told Live Science.
According to the study, published Nov. 18 in the Journal of Maritime Archaeology, Castro and his colleagues now hope to verify their identification, in part by conducting an archaeological survey of the coral reefs that stretch north from Malindi to Ras Ngomeni, Kenya — a distance of about 15 miles (25 kilometers).
The wreck lies about 1,640 feet (500 meters) from the shore, at a depth of about 20 feet (6 meters). Little of it can be seen amid corals on the seabed, but Castro and other divers unearthed timbers from the ship's hull and frame in two archaeological trenches they made at the submerged site.
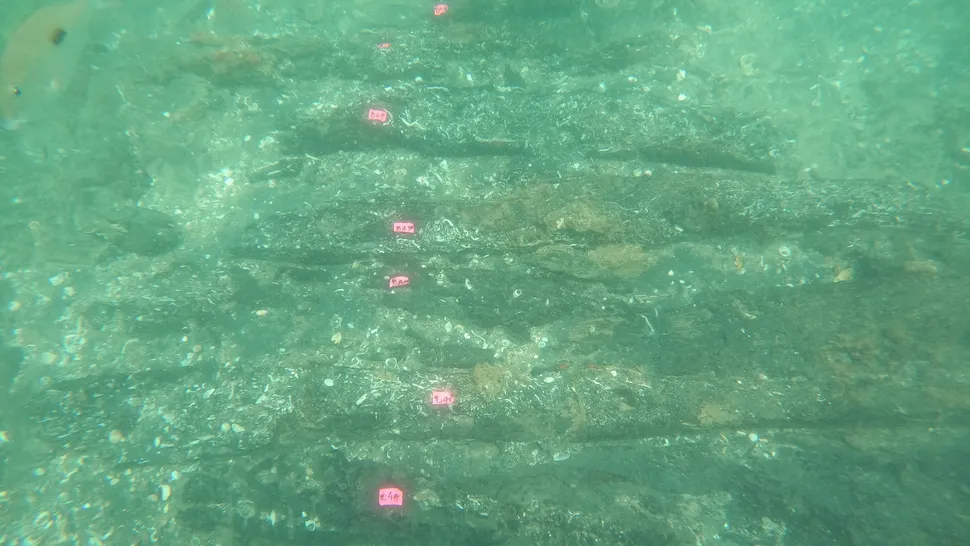

Underwater archaeologists think the wreck is the São Jorge, a Portuguese ship that sank in 1524 during Vasco de Gama's final voyage into the Indian Ocean.
(Image credit: Filipe Castro)
Portugal to India
Da Gama (lived circa 1469 to 1524) pioneered the route from Europe into the Indian Ocean in 1497, when his ship was the first to round the Cape of Good Hope at the southern tip of Africa.
Da Gama (lived circa 1469 to 1524) pioneered the route from Europe into the Indian Ocean in 1497, when his ship was the first to round the Cape of Good Hope at the southern tip of Africa.
The Portuguese explorer made three more journeys along the route before his death in India in 1524, possibly from malaria, and his explorations were the basis of the Portuguese trading empire in the Indian Ocean.
The São Jorge was one of about 20 ships that joined da Gama for his final voyage in 1524, but it sank shortly before his death.
The São Jorge was one of about 20 ships that joined da Gama for his final voyage in 1524, but it sank shortly before his death.
The new study suggests it was one of two early Portuguese ships that sank near Malindi; the other was Nossa Senhora da Graça, which went down in 1544.
If the wreck near Malindi can be confirmed as the São Jorge, it would have "significant historical and symbolic value as physical testimony to the presence of Vasco da Gama's third armada in Kenyan waters," Castro said in a statement earlier this year.
"I think this is a unique shipwreck," he told Live Science.
If the wreck near Malindi can be confirmed as the São Jorge, it would have "significant historical and symbolic value as physical testimony to the presence of Vasco da Gama's third armada in Kenyan waters," Castro said in a statement earlier this year.
"I think this is a unique shipwreck," he told Live Science.
"It is a treasure."

The Vasco da Gama Pillar in Malindi, Kenya, was erected by the Portuguese explorer Vasco da Gama. It was erected for navigation purposes and to indicate their visit in Malindi.
Mystery wreck
Kenyan authorities were interested in the Malindi shipwreck, Castro said, and the site may be developed as an underwater museum.
The wreck was discovered in 2013 by Caesar Bita, an underwater archaeologist at the National Museums of Kenya, who recovered copper ingots and elephant tusks from the submerged site.
Bita is now helping to coordinate the ongoing investigation, Castro said.
The wreck would be "archaeological stardust" if it proved to be the São Jorge, said Sean Kingsley, a maritime archaeologist and the editor of Wreckwatch magazine, who is not involved in the project.
"Kenya was a staging post for tapping into the dazzling wonders of the Indies," so any early European shipwrecks found there are "hot property," he told Live Science in an email.
However, further archaeological investigations will be necessary to determine whether this was one of da Gama's ships.
The wreck would be "archaeological stardust" if it proved to be the São Jorge, said Sean Kingsley, a maritime archaeologist and the editor of Wreckwatch magazine, who is not involved in the project.
"Kenya was a staging post for tapping into the dazzling wonders of the Indies," so any early European shipwrecks found there are "hot property," he told Live Science in an email.
However, further archaeological investigations will be necessary to determine whether this was one of da Gama's ships.
"This is one wreck that screams out for protection, respect and care before its back story vanishes forever," Kingsley said.
Links :
- LiveScience : 32 haunting shipwrecks from the ancient world / 30 incredible sunken wrecks from WWI and WWII /
- Popular Mechanics : An Uncovered Wreck May Be the Long-Lost Ship From Vasco da Gama’s Final Voyage
- CFE : CFE researcher believes he has found a Vasco da Gama galleon
- Ancient Origins : Shipwreck off Kenyan Coast May Have Been Vasco da Gama’s São Jorge
- GeoGarage blog : 500 years later, sunken pirate ship from explorer Vasco da Gama's fleet discovered
No comments:
Post a Comment