From Forbes by Marshall Shepherd
Here is something that you can take to the bank.
We will not see the name "Dorian" used in the Atlantic basin for any future hurricane.
The names of particularly destructive or impactful storms are retired.
Seas warmer than 27.8°C (82°F) are generally considered hurricane fuel.
HurricaneDorian is now at Category 3 strength.
Although the route of Dorian is uncertain, one thing is for sure: it has plenty of warm water on any path it takes.
According to the National Hurricane Center, Dorian is now tied with the 1935 Labor Day hurricane for the strongest Atlantic hurricane landfall on record. In a 3 pm advisory on September 1st, the National Hurricane Center warned of gusts to 220 mph and 18 to 23 feet storm surges for parts of the Abacos.
I have been in the field of meteorology over 25 years and do not recall seeing warnings about 220 mph gusts for a hurricane.
Hurricane watches have also been issued for Andros Island and from North of Deerfield Beach to the Volusia/Brevard County Line in Florida. At the time of writing, the official forecast from the National Hurricane Center is for a northward curve and no direct Florida landfall.
Hurricane Dorian putting on a lightning show tonight Aug 30th.
Spectacular imagery.
source Dakota Smith
Hurricane Dorian putting on a lightning show tonight Aug 30th.
Spectacular imagery.
source Dakota Smith
This is dramatically different from forecasts only a few days ago.
There is still uncertainty with the forecast so coastal Florida, Georgia, and the Carolinas should remain on high alert.
Why has the track forecast been so challenging with Hurricane Dorian?
Hurricane Dorian approaching the Abaco
NOAA/CIMSS
NOAA/CIMSS
Historically, hurricane track forecasts have outpaced intensity forecasts.
I discuss the reasons why in a previous Forbes article at this link. With Hurricane Dorian, uncertainty about the forecast track and timing of the storm forced officials to move the Florida State - Boise State football game from Jacksonville, slated for a 7 pm kickoff on Saturday, to noon in Tallahassee.
I am certain that many businesses and people are questioning the move given that timing of when impacts are now expected.
Unfortunately, officials and emergency managers often must make decision on the best information at the moment.
Some people may be tempted to use uncertainty with this forecast to spew vitriol or skepticism at meteorologists and our models.
However, challenges with Hurricane Dorian's track forecast do not define the legacy of weather forecasts.
It would be silly to say that the NFL's best field goal kicker is terrible based on a few misses.
NOAA's GOES-East took this image of Hurricane Dorian the evening of September 1, 2019.
see animation
see animation
So what's going on? I asked a panel of tropical meteorology experts.
Speed of motion of Hurricane Dorian has been a significant challenge.
Before you bash the meteorologists for being stupid: one reason the forecasted track has changed is because the forecasts of the forward speed of Dorian have slowed it down more and more.
If it had chugged along as originally forecast, it likely would have hit east-central Florida and then maybe gone into the Gulf, before the high pressure above us in the Southeast would break down.
But, because it's moving more slowly, the high-pressure break down is opening the gate, so to speak, for Dorian to go more northward and eastward.
So, the change in forecast is tied tightly to the arrival timing.
He wrote:
the ridge to the north of Dorian has been steering Dorian off to the west the last few days....But there is a weak trough that is swinging into the eastern US that is going to erode the strength to the ridge enough so that a gap forms to the north of Dorian and it begins to move further to the north.
The timing of when that weakness develops and on how far Dorian makes it west in the meantime has been the source of uncertainty in the model guidance for the last 2-3 days according to Papin.
At the time of writing, there is still some spread in the model solutions.
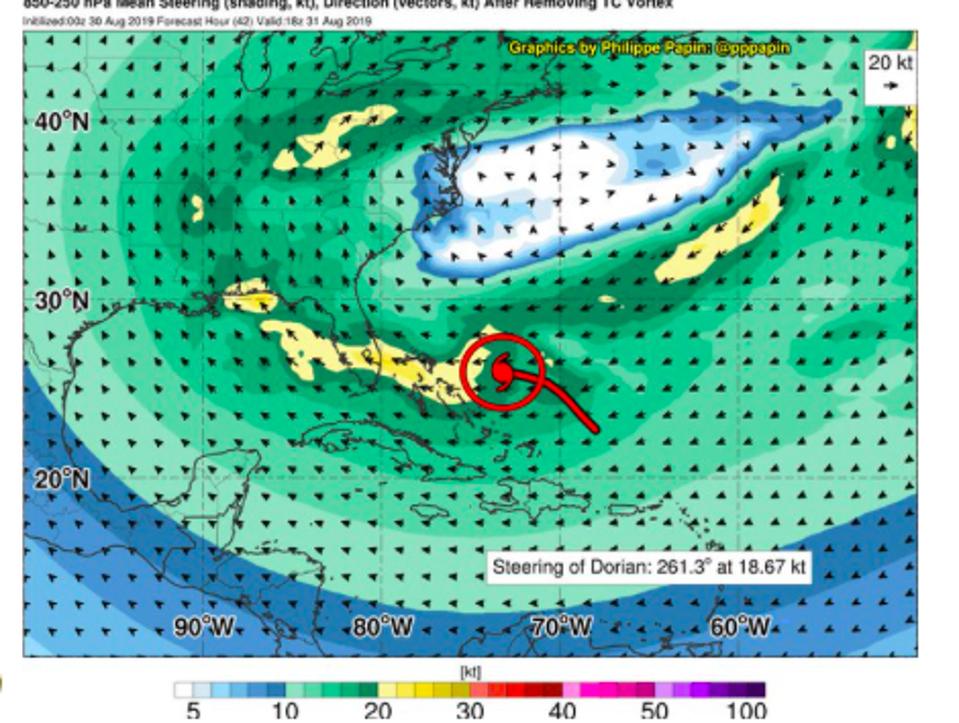
Interaction of high pressure ridging with Hurricane Dorian
Philippe Papin
Dr. Michael Ventrice is a tropical weather expert with IBM and The Weather Company.He has been concerned about the storm environment and how well the models are capturing the rapidly evolving situation.
He told me:
I believe the uncertainty is derived from how the models are resolving Dorian, locally.
The recent intensification of the storm today is not being resolved by the models properly at the time of the 12z initialization.
The interaction with the Bahamas, how that interaction might alter the mesoscale structure of the Hurricane, if that interaction induces a wobble, are all valid questions at this point in time
Michael Ventrice — IBM/The Weather Company
A hurricane of this size and intensity can certainly modify its environment and be modified by that environment.
Sam Lillo, a doctoral candidate at the University of Oklahoma, tweeted an interesting point on the afternoon of September 1st about how worrisome the rapid intensification and track uncertainty of Hurricane Dorian has been:
The track uncertainty in NWP at under 3-day lead-time is very uncomfortable, especially considering proximity to land. This would be uncomfortable for any hurricane. But then make it a category 5.
Sam Lillo, doctoral candidate in meteorology at the University of Oklahoma
Following hurricane Dorian through wave height
Hurricane Dorian, the most powerful hurricane to hit an Atlantic island on record - projected significant wave height of 11.2 metres by September 5th, from Copernicus Marine Service Waves model.
Hurricane Dorian, the most powerful hurricane to hit an Atlantic island on record - projected significant wave height of 11.2 metres by September 5th, from Copernicus Marine Service Waves model.
Our best models have oscillated (and in some cases continue to do so) within the past 24-36 hours on just how close Dorian will get to Florida before curving northward.
Lillo offers some further insight into what Dr. Ventrice was alluding to about the environment:
As Dorian strengthened faster than expected, diabatic outflow developed an upper level anticyclone to the southwest, adding southerly and westerly components to the steering flow.
The westerly component in particular slowed the forward motion of the hurricane, and now its track across the Bahamas coincides with a trough that sweeps across the Mid Atlantic and Northeast on Monday.
This trough cuts into the ridge to the north of Dorian, with multiple steering currents now trying to tug the hurricane in all different directions.
The future track is highly sensitive to each of these currents, with large feedback on every mile the hurricane jogs to the left or right over the next 24 to 48 hours.
Sam Lillo, doctoral candidate in meteorology at the University of Oklahoma
Lillo offers a nice meteorological explanation.
In a nutshell, he is saying that the rapid intensification perturbed the near-storm environment and now there may be other steering influences besides the ridge of high pressure that the models are struggling to resolve.
In a previous Forbes piece last week, I mentioned that forecasts in the 5+ day window and beyond can have errors of 200 miles and that the information should be used as "guidance" not "Gospel." Because there is still uncertainty with the models and Dorian is such a strong storm, residents from coastal Florida to the Carolinas must pay attention and be prepared to act.
I have complete confidence in my colleagues at the National Hurricane Center, and they should always be your definitive source with storms like this.
They still maintain an eventual curve northward before the storm reaches the Florida coast.
However, the issuance of hurricane watches in Florida also indicates that they know the margin of error is razor thin.
Links :
- WSJournal : Why Hurricane Dorian Is So Hard to Track
- NYTimes : Hurricane Dorian forecast map / Those Hurricane Maps Don’t Mean What You Think They Mean
- CTVnews : How forecasters track Hurricane Dorian
- NPR : Historic Hurricane Dorian Bears Down On Northern Bahamas As A Category 5 Storm
- LiveScience : Why Is Hurricane Dorian's Path So Tricky to Predict?
- The Economist : How global warming makes hurricanes more severe
- CNN : Here's what Hurricane Dorian is expected to do as it approaches land / Will Dorian hit Florida? The path is uncertain but officials say to get ready





Wired : Why Hurricane Dorian Defied Forecasts and Sank The Bahamas
ReplyDeleteTampaBay : Hurricane Dorian forecasting shows how models have improved since Floyd in 1999
ReplyDeleteNYTimes : The Bahamas, Before and
ReplyDeleteAfter Hurricane Dorian
CNN : Hurricanes travel 17% more slowly than they did 75 years ago. Here's why
ReplyDeleteSMH : Slow, intense and unrelenting: The science behind Dorian's most dangerous qualities
ReplyDeleteBathymetry charts of Gran Bahama & Abaco
ReplyDeleteThe Hull : Hurricane Dorian highlights urgent need for improved forecasts
ReplyDeleteCityLab : Yes, Maps Can Lie. But Not Like This
ReplyDelete