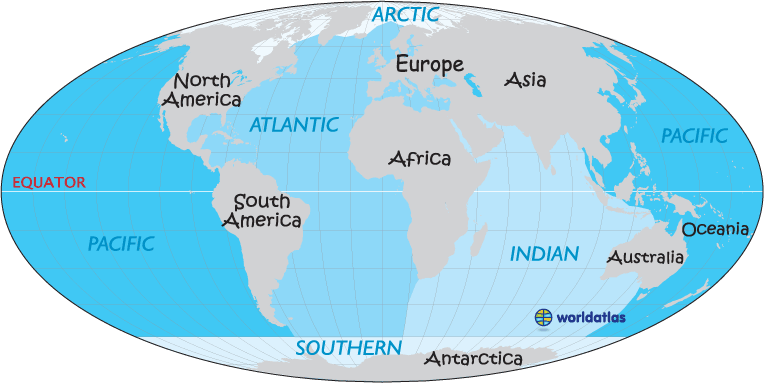
World map ocean locator
From World Atlas by Antonia Cirjak
Earth can have anywhere from 1 to 7 oceans, depending on how you look at it.
There is one global ocean called the World Ocean, because the entire body of water on our planet is connected.
Nowadays, it is widely accepted that the Earth has five oceans: the Arctic, Atlantic, Indian, Pacific, and the Southern Ocean.
The largest and the deepest ocean on our planet is the Pacific Ocean.
This ocean extends all the way from the Arctic to the Southern Ocean from north to south and is bound by the Americas in the east and Asia and Australia in the west.
Earth can have anywhere from 1 to 7 oceans, depending on how you look at it.
Yes, there is one global ocean called the World Ocean, because the entire body of water on our planet is connected.
It covers 71 percent of the surface of our planet, but we usually divide it into distinct regions, all named accordingly.
The Earth has five oceans: the Arctic, Atlantic, Indian, Pacific, and the Southern Ocean.
Over time, the boundaries we use to determine these regions have evolved due to various geographical, cultural, and historical reasons.
Nowadays, it is widely accepted that the Earth has five oceans: the Arctic, Atlantic, Indian, Pacific, and the Southern Ocean.
1. Arctic Ocean
Out of the five major oceans on our planet, the Arctic Ocean is the smallest and the shallowest one.
It is also the coldest one, which makes sense considering its geographical position.
Some oceanographers consider it a sea, but it is recognized as an ocean by the International Hydrographic Organization.
It is the northernmost part of the World Ocean, found in the Arctic north polar region.
It is surrounded by the continents of Eurasia and North America and is covered in sea ice in some parts.
The ice melts during specific times of the year, which can influence the temperature and salinity of the ocean.
On average, the Arctic Ocean has the lowest salinity out of all the five oceans.
2. Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest ocean, and its area is determined to be 106,460,000 square kilometers.
This ocean covers about 20 percent of the surface of our planet.
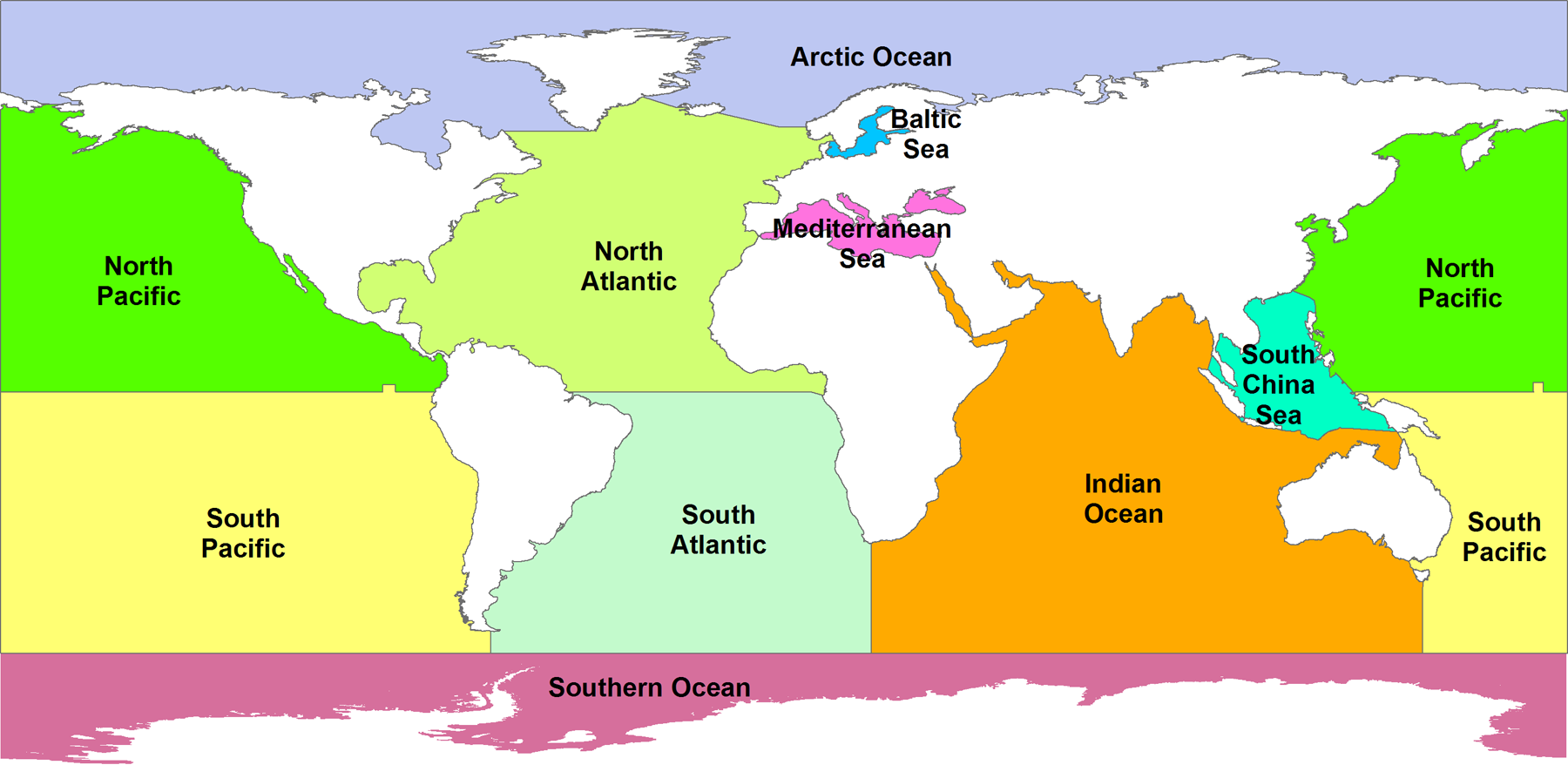
The Atlantic Ocean is often looked at as the boundary between the “Old World” and the “New World.” It is shaped in the form of the letter “S,” and it occupies the space between North and South America to the west and Europe and Africa to the east.
It is also connected to all other oceans directly, so it can be considered the middle component of the World Ocean.
There were many famous explorations of this ocean throughout human history, such as the Challenger expedition and the German Meteor expedition, among others.
From IHO 23-3rd: Limits of Oceans and Seas, Special Publication 23, 3rd
Edition 1953, published by the International Hydrographic Organization.
3. Indian Ocean
As the third-largest part of the World Ocean, covering 70,560,000 square kilometers, the Indian Ocean makes up for almost 20 percent of the water on the surface of our planet.
Asia surrounds this ocean on its north side, Africa, on the west, and Australia to the east.
On its south side, it is connected and wounded by the Southern Ocean.
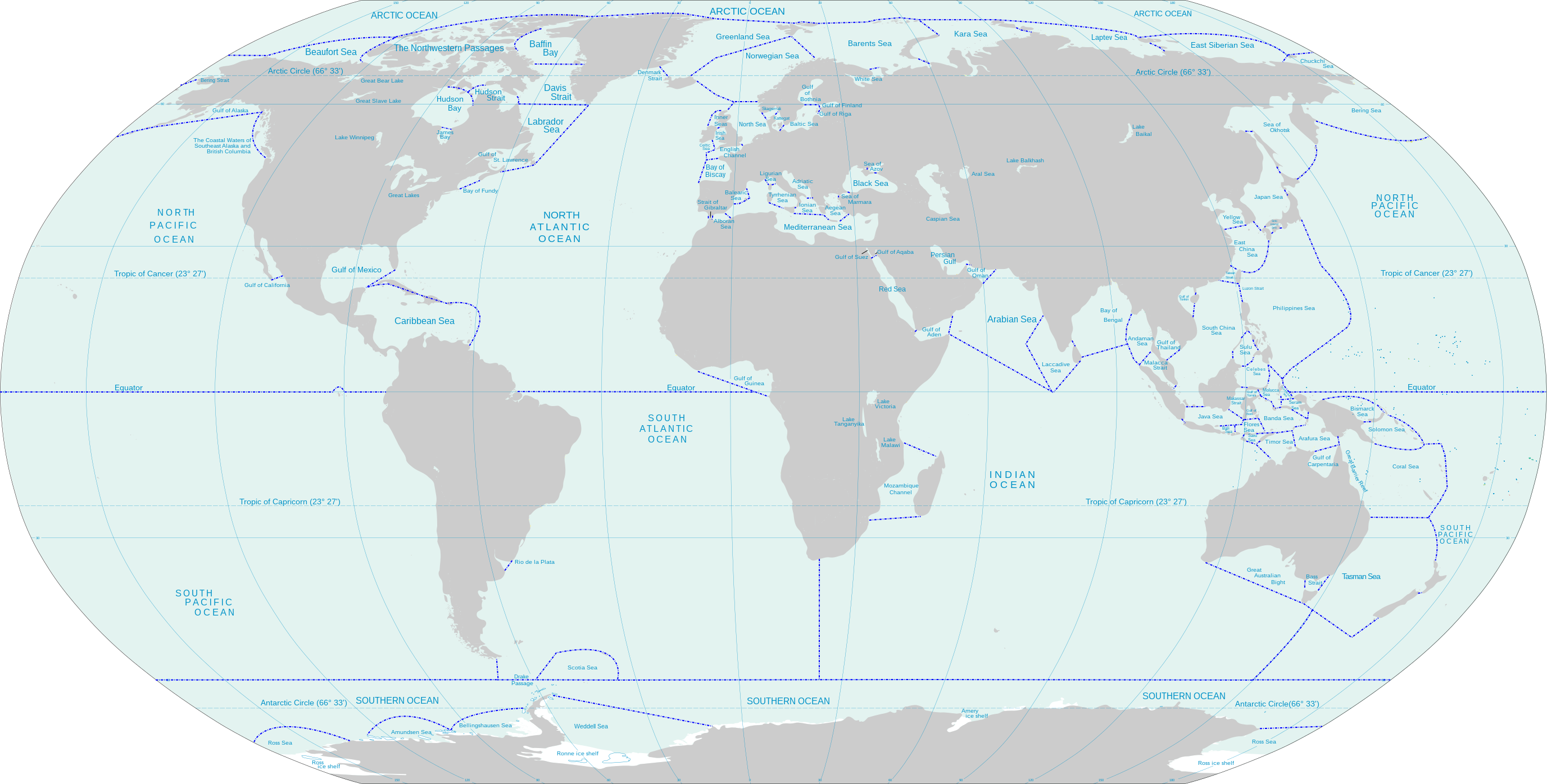
Many regional seas can be found along with the core of the Indian Ocean, such as the Somali Sea, the Bay of Bengal, the Arabian Sea and the Laccadive Sea.
Monsoons and cyclones mostly dictate the climate in this ocean.
The Indian Ocean is the warmest out of all the five oceans on our planet, and it is known as a fruitful fishing ground.
4. Pacific Ocean
The largest and the deepest ocean on our planet is the Pacific Ocean.
This ocean extends all the way from the Arctic to the Southern Ocean from north to south and is bound by the Americas in the east and Asia and Australia in the west.
The size of this ocean is 165,250,000 square kilometers, which makes it the largest part of the World Ocean.
The Pacific Ocean covers 32% of the surface area of our planet, which means that it is larger than all of the land area on Earth when combined.
This ocean is usually divided into two subdivisions by the equator.
These are the Northern and the Southern Pacific Oceans.
On average, the depth in the Pacific Ocean is 13,000 feet.
It also features the deepest point in the world, the Challenger Deep that can be found in the Mariana Trench, and that reaches the depth of 35,853 feet.
Not only that, but the ocean also features the second and the third deepest points on our planet, the Horizon Deep (35,509 feet) and the Sirena Deep, respectively.
5. Southern Ocean
This ocean encircles the continent of Antarctica, and it is the second smallest of the five oceans.
The Southern Ocean is known as being the zone where the colder waters from the Antarctic that are flowing northwards mix with the warm waters from subantarctic regions.
Throughout history, many have debated whether the Southern Ocean should be considered an ocean at all.
Many believed that it does not exist and considered it just to be various parts of other oceans.
However, in time researchers managed to discover how important Southern Circulation is and since this body of water-limited that circulation, they called it the Southern Ocean, thereby confirming that it does exist after all.
Links :
- World Atlas : Oceans Of The World By Size


No comments:
Post a Comment