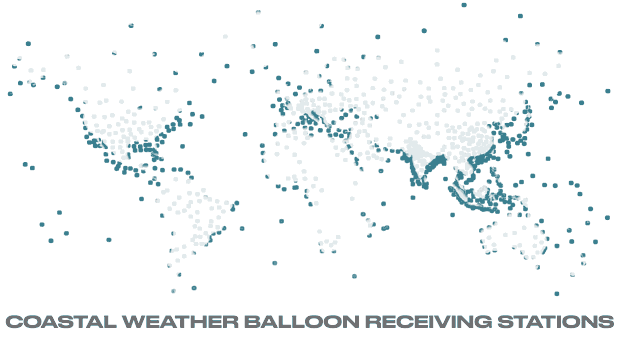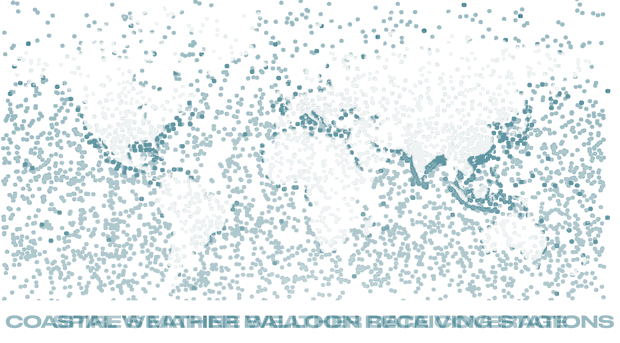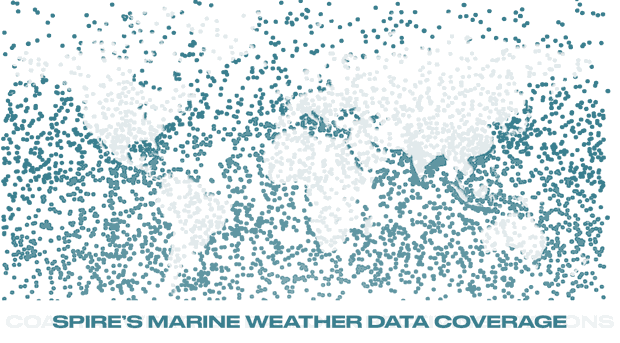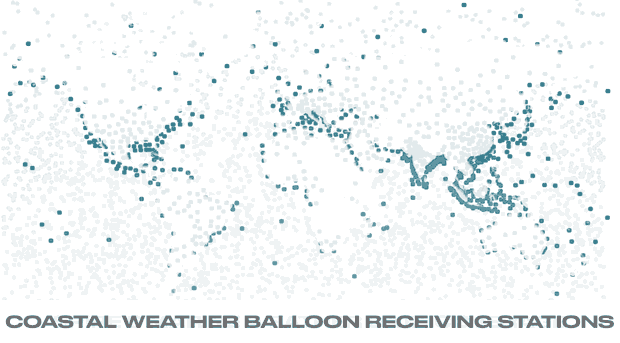
One in five fish are now caught illegally.
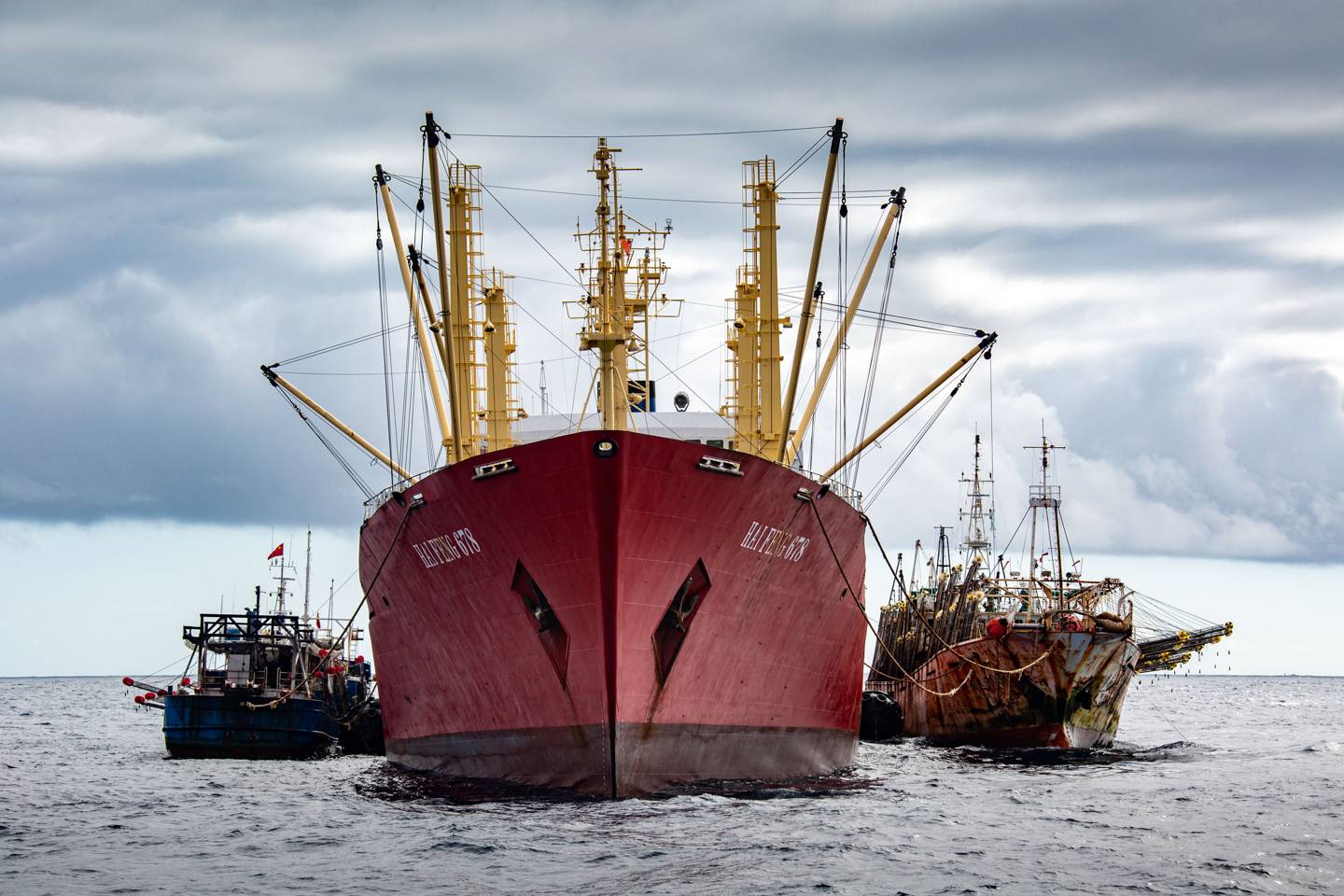
Chinese crawlers tie up to a 'reefer' – the refuelling and offloading vessels that service the long-distance fleets
From Wired by Olive Heffernan
When trawlers turn off their transponders, they "go dark", allowing them to hide illicit activity such as illegal fishing and modern slavery.
Now, a team of ocean experts is using satellite data to light them back up
One Wednesday in March, 2019, a small group of ocean experts gathered in a conference room in Panama City’s Waldorf Astoria, ready to take the stage.
Outside, the weather was hot and muggy and the streets dirty with rubble from nearby roadworks.
Inside the cool, marbled interior of one of the city’s glitziest hotels, government officials from Panama, Ecuador, Colombia and Costa Rica sat on cream chairs in neat rows, listening intently.
First came the usual formalities: welcome addresses and statements of intentions to collaborate.
About halfway through the morning’s proceedings, it was Bjorn Bergman’s turn.
Bergman was sharply dressed for the occasion and looked serious as he addressed the delegates in effortless Spanish.
He was a data analyst at Global Fishing Watch (GFW), an environmental non-profit that, in 2016, started using satellites to track vessels at sea.
Ships of a gross tonnage of 300 or over are required, in international waters, to carry the Automatic Identification System (AIS) transponder, to avoid collisions.
Picked up by satellite, these communications can also be used to detect a ship’s movements.
Using this data, GFW mapped global fishing patterns for the first time, working out that around 55 per cent of the ocean is being fished.
With this same method, it has been able to visualise approximately 80 per cent of boats fishing international waters.
The other 20 per cent have been untraceable – in part because some nations, such as Canada, don’t insist on fishing vessel owners using an AIS at all, and most small boats (such as 90 per cent of the Indonesian artisanal fleet) aren't required to carry AIS.
However, some fishers simply turn off their transponders if they don’t want to be seen – a practice known as "going dark".
Fishers often cite competition as a reason for wanting to keep their location secret, but, in such cases, going dark is only a temporary measure.
The invisible fleet – also called "dark targets" – are vessels that are untraceable for long periods, maybe weeks or months at a time, and are presumed to be avoiding detection.
“We knew there was a dark fleet – that a lot of fishing in the world is not very easily trackable,” says David Kroodsma, head of research at GFW.
“The oceans are a common resource and when it's really difficult to track who's fishing, people are going to take advantage.”
Bergman had been hunting these dark targets relentlessly for several years.
However, one particular fleet of around 300 vessels – mostly Chinese squid trawlers – kept evading him.
Centred in a remote part of the South Pacific, beyond national waters, the fleet was hiding dark targets, which Bergman suspected were operating illegally.
As part of the fleet there were large refrigerated cargo boats – known as reefers – used for refuelling and offloading catch.
While that in itself is perfectly legal, "transhipment" of a boat’s catch is often an indicator of crime.
For a start, it’s an easy way of hiding poached fish, and other contraband, among legal catch.
Furthermore, it allows for ships to spend long periods away from land, hinting at the use of slave labour, something that is rife in long-distance fishing fleets.
The reefers enabled this fleet, with around 6,000 men, to stay at sea for a year or more.
Bergman knew that many of these reefers were carrying the Panama flag.
Under international law, all merchant ships must have a "flag state" or a country to which they are registered.
For a fee, Panama allows any ship to fly its flag, regardless of where it was built, or the country in which its owner – or indeed any crew member – lives: this is called a "flag of convenience".
The advantages of this include low (or no) income tax, access to cheaper labour, and obscuring the true ownership of a vessel or fleet.
Bergman’s message was simple: they needed Panama, a renowned secrecy jurisdiction, to share private data from its register, allowing Panama-flagged fishing vessels to be tracked across the global ocean.
Among these vessels were possible dark targets – vessels that were off-the-radar, avoiding detection and presumed to be acting criminally.
If Panama could share its data, GFW could expose pirate vessels.
As Bergman explained, it could also help Panama to stop piracy in its own waters.
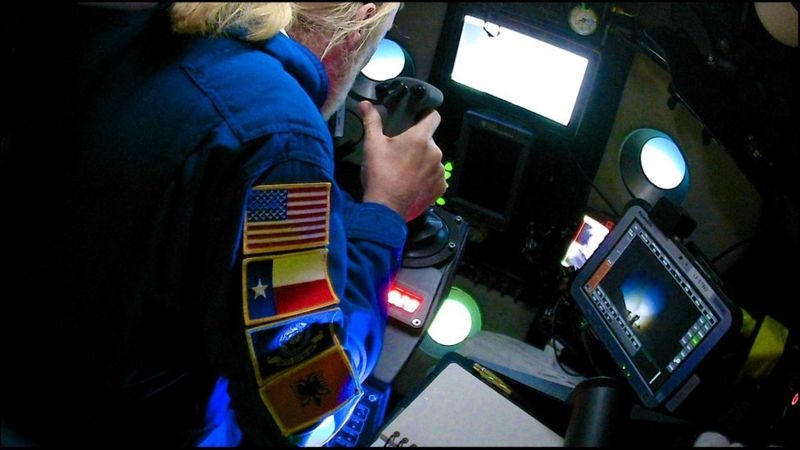
Bjorn Bergman on the trail of 'dark targets'
credit : Simon Ager
There are numerous ways in which trawlers take illicit catch – intentionally playing down its value, targeting waters where no quotas have been set, or pillaging directly from protected waters, for example.
With one in five fish now caught illegally, and with 93 per cent of commercial stocks now fully- or over-exploited, the drive to end pirate fishing has never been greater.
“It's no secret that we have this massive overfishing problem.
And illegal fishing is a large part of that, so it seems pretty clear that this is something we should try to eliminate,” says Peter Hammarstedt, a conservationist and boat captain with Sea Shepherd, a non-profit ocean conservation organisation (with a track record in direct action) based in Washington state, in the US, and Melbourne, Australia.
Pirate fishing also points to human rights crimes such as slavery, brutality and forced labour.
China is acuused of being the worst offender by the NGO Global Initiative Against Transnational Organised Crime.
In recent years, Chinese reefers have been caught illegally trans-shipping catch, such as sharks, in the Pacific.
In 2019, four dead crew were offloaded from Chinese and Taiwanese trawlers at the Port of Montevideo in Uruguay.
Two of the vessels are repeat offenders.
China’s distant-water fleet dwarfs all others, outsizing the US fleet by a factor of ten.
Having emptied its own coastal fisheries, China has turned to other national waters and the high seas, targeting high-value tuna, sharks and squid.
Its squid jiggers focus on two species – Humboldt and Argentine shortfin – regarded as among the most heavily fished in the world.
“It’s only relatively recently that they started doing this, and so we have no idea of the implications of hundreds of ships fishing squid this intensively,” says Bergman.
One worry is that it will deplete the squid stocks that South Americans depend on for food and work.
And that may be why, for Bergman, the quest to find and stop dark targets is a personal one.
As a child, Bergman lived for a number of years with his family in Peru, a country that is bearing the brunt of China’s aggressive overseas fishing policy.
Later, in secondary school, he visited for summer holidays with his father, who was a National Geographic-funded researcher investigating agriculture in the high Andes.
Bergman recently returned to live there, after many years in the US and Sweden.
After college, he moved to Alaska to work as a fisheries observer.
“It’s a job that you could start out in; they needed to recruit people because they had really high attrition.
So they're always trying to bring people into the programme,” he says.
The job was varied; at times he’d join family-run operations for trips of three to four days from Kodiak Island, which he really enjoyed.
But he also went on longer trips, of a month or so, on large industrial boats, working some of the ocean’s most dangerous fisheries.
“It was just a really difficult experience,” recalls Bergman.
By most accounts, working as an observer can be gruelling.
Since 2007, at least nine fisheries observers, including four Americans, have died on the job.
Foul play is suspected in at least two of these cases.
Many observers experience intimidation and bribery; others witness horrendous abuse.
After several years, Bergman was done.
He thought about going into academia – having by then completed a Master’s in cell biology – but he saw that environmental non-profit SkyTruth was recruiting analysts to work with fisheries data and decided to apply.
SkyTruth was founded by geologist John Amos with the idea of using satellite imagery to improve environmental accountability.
By 2014, Amos and Paul Woods, SkyTruth’s Chief Technology Officer – friends and neighbours from Shepherdstown, West Virginia – had made huge headway tracking the visible impacts of industry from space.
In 2010, they had gained acclaim as the first to challenge BP’s reports of the extent of oil pouring into the Gulf of Mexico from the Deepwater Horizon blow out, the largest accidental oil spill in history.
But one area they’d made little progress in was fishing.
Amos and Woods realised there was untapped value in an existing data set – the satellite detections of boats that use AIS.
At that point, maps of global fishing were notoriously unreliable, largely based on where biologists had found particular species.
The AIS system filled that gap.
Designed as a means for captains to relay their position to other vessels, AIS could be co-opted to track a ship’s movements, shining a light on global fishing patterns.
“We realised there was this huge data source of satellite AIS that covered the globe.
In the same way that we could measure features on land and see a change in land use, we looked at this and immediately knew we could use it to measure how people are using the ocean,” says Woods.
The simplicity of this approach was that AIS data was not only global but freely available, unlike the data from VMS (Vessel Monitoring System), a comparable satellite-based system for routinely logging a ship’s position, name and call sign.
Most nations mandate their larger domestic vessels carry VMS on board, but the system is expensive and the data usually proprietary, held by governments such as Panama's.
In 2014, Amos and Woods teamed up with Google and the marine conservation organisation Oceana to found Global Fishing Watch.
The following year, they hired Kroodsma, an experienced ocean scientist, to lead their research programme.
For data analysis, they brought in Bergman.
Despite having spent years on boats, it turned out that Bergman, a quiet, unassuming character, was deeply interested in the intellectual challenge of digging into the data.
And he was very good at it, possessing a natural ability to see patterns and anomalies.
GFW had more than 60 million data points per day on AIS vessel locations from satellites.
From their configurations, Bergman could simply look at the ship tracks on AIS and tell whether the boat was in transit or fishing – and if it was fishing, whether it was trawling, longlining (a trailing line with baited hooks at regular intervals) or purse seining (creating a net "cage" around the fish).
“Bjorn, having been on fishing vessels out in the Bering Sea, was able to look at those data and say ‘Hey, I know what they’re doing right now’,” says Amos.
In January 2016, of the 120,000 vessels at sea, Bergman noticed six that looked suspicious.
They were Chinese longliners fishing a remote part of the southern Indian Ocean, close to the search site for the lost Malaysian passenger plane MH370.
It wasn’t an obvious location for a fishing fleet, and “they were moving in a way that I wasn’t familiar with,” says Bergman, who noticed an unusually high number of AIS signals coming from the area.
“When I looked closer, I could see them laying out a long string of AIS beacons and then reeling them in”, he says.
Bergman contacted the local fisheries registries, but none of them recognised the vessels.
That was enough to raise the alarm.
From SkyTruth’s office in West Virginia, Bergman wrote a blog post detailing the suspect behaviour.
Over in Perth, Australia, Sea Shepherd captain Sid Chakravarty read Bergman’s blog and immediately launched a patrol mission.
What he discovered was shocking – the entire fleet was using banned drift nets laid out over kilometres of ocean, ensnaring species such as tuna, sharks, turtles and dolphins.
The trawlers were attaching AIS beacons to the nets so as not to lose them, which explained the pattern Bergman had noticed from his landlocked position in the US.
The activists intercepted the fleet, hauled in some of their nets and videoed them.
After that, the ships scattered and went dark.
But a month later, one boat turned on its transponder again, allowing Bergman to relay an updated position to Sea Shepherd.
The team ended up chasing the vessel for 8,000km across the ocean to the Chinese port of Zhuhai, where the entire fleet was eventually detained and suspended.
The fleet owner was fined nearly a million dollars (£800,000) by the Chinese authorities.
“It’s tremendously valuable to have a witness on the ocean,” says Bergman.
“We have a lot of data sources, but we need to corroborate some of what we are seeing, so that we can be sure we are drawing the right conclusions.”
Bergman had also learnt to identify other suspicious behaviours, such as unusual fishing locations, and to chart a ship’s most likely course from satellite data, in a way that most analysts were simply unable to.
In August 2017, for example, Bergman got a call to say that the Ecuadorian navy had just intercepted a vessel near the Galapagos islands.
A Chinese-flagged reefer, the Fu Yuan Yu Leng 999, had repeatedly refused to respond to radio calls from the navy, and so a helicopter and coast guard boat were dispatched to take a closer look.
On boarding the vessel, the officers were stunned to find more than 6,000 dead sharks – the largest seizure of sharks in the history of Galapagos.
Despite the arrest, it wasn’t known where the sharks – some of which were endangered – were caught, or what other boats the trawlers had liaised with.
“Just having sharks on a boat in Galapagos is illegal, but they also wanted to know how they got them,” explains Bergman, who set about retracing the movements of the Fu Yuan Yu Leng 999.
During his trial in Ecuador, the captain named two Taiwanese vessels as the source of the sharks.
But Bergman could see from the data that the reefer had a rendezvous with four Chinese longliners to the west of Galapagos.
“He clearly gave false testimony at the trial,” says Bergman.
The ship’s owner was fined US$5.9 million and the captain sentenced to four years in prison.
Last year, a crew member from one of the Chinese longliners confirmed that Bergman was right; they had offloaded their catch on to the Fu Yuan Yu Leng 999.
credit : Simon Ager
As a detective of the seas, Bergman seemed to be able to solve pretty much all cases that were presented to him.
Except for one.
He first noticed the fleet of Chinese squid jiggers in 2014.
The vessels were fishing along the boundary of Peru’s national waters, but suddenly, in 2017, the entire fleet unexpectedly shifted to a position in the South Pacific.
Some of the ships were not broadcasting AIS, making it impossible to know just how large the fleet was and what it was doing.
This case was different, and – from an analysts’ perspective – especially exciting.
Ordinarily, with dark targets, Bergman has to rely on vessels switching on their transponders to gauge their whereabouts.
But with the squid jiggers, which use lights to attract squid to the boat, there was another possibility.
In 2017, a research scientist named Chris Elvidge, who leads Earth observations at the National Ocean and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), one of the US research agencies, approached GFW with an idea: he had been developing a system to detect sources of light from space at night, making use of a satellite sensor called Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS).
He now wanted to see whether the lights used for squid jigging could help pick out some of the dark targets in Indonesian waters.
To test his idea, Elvidge needed Indonesian VMS data.
At that stage, GFW had just signed an agreement with Indonesia that would make its VMS data public.
The agreement was the first of its kind and would add 5,000 vessels to the team’s global fishing map.
It was a huge win in the team’s fight for transparency and was largely made possible by Indonesia’s minister for fisheries, Susi Pudjiastuti, who has taken a hard line against illegal fishing.
“The release of Indonesia’s VMS data was a big deal. That kind of broke a glass ceiling,” says Woods, who is now CTO with GFW.
Since taking office in 2014, Susi Pudjiastuti has seized and destroyed more than 300 illegal vessels found fishing in Indonesian waters.
(She’s also become known for her viral videos, which show her drinking coffee while paddle boarding, and dancing on board a naval vessel.)
Woods persuaded the Indonesians to hand Elvidge their VMS data, which NOAA then matched to its VIIRS vessel detections.
In 2018, GFW rolled out VIIRS data over the ocean, allowing Bergman and the rest of the team to see many boats that had, up to this point, been entirely dark.
Unlike AIS and VMS, VIIRS can’t tell the identity of a boat; it can just pick up a light signal which can then be compared against AIS or VMS data to see if the ship is broadcasting.
For the first time, Bergman was able to detect some of the dark Chinese squid fleet.
However, that still wasn’t enough to track all the vessels.
At this point, Bergman had no alternative: he was going to have to hunt them on the high seas.
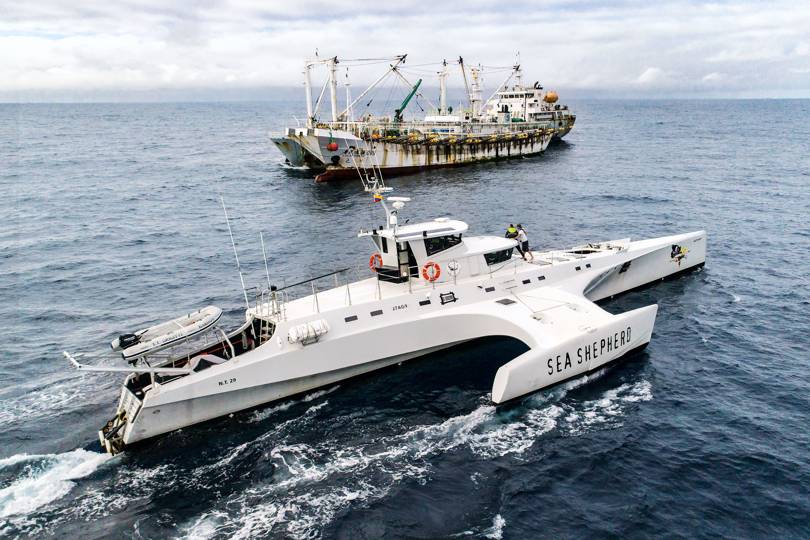
On September 12, 2018, Bergman joined the MR Brigitte Bardot – a vessel operated by Sea Shepherd.
Travelling with Bergman was Eloy Aroni, a Peruvian researcher who was just finishing his thesis on tracking the squid fleet using VIIRS.
Looking ahead, Bergman and Aroni could see that some boats were visible on VIIRS, but not on AIS.
They still, however, had several days of travel before they reached their targets.
On September 19, they rounded the north cape of the island of Isabela, the largest of the Galapagos, and headed west into a vast stretch of the open Pacific.
Ahead of them, the nearest landfall was the Marquesas islands of Polynesia, some 3,000 nautical miles away.
They were venturing into one of the most remote parts of the planet on a voyage that would ultimately bring Bergman into contact with one of the world’s darkest fishing fleets.
But in a fleet 300-strong, like the one fishing the South Pacific, not all boats are squid jiggers.
Some are reefers, whose job it is to restock the fishing boats and to transship the catch.
To identify the reefers, Bergman had to use another data source: Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imagery.
Usually acquired from the European Space Agency’s Sentinel-1 system, the advantage of radar imagery is that it can pick out large objects with metal hulls, such as medium-size trawlers, that are neither broadcasting their position nor displaying visible lights from space.
There are some downsides, however: SAR data is hugely expensive and users have to weed out other objects that, on radar, look just the same as boats, such as wind farms, oil and gas rigs, and icebergs.
Before heading out to the high seas, Bergman had snagged a couple of rare radar images of the fleet, taken from Canada’s RADARSAT-2 satellite.
This meant he had three data sources - AIS, VIIRS night imagery and radar – which he could use to find dark targets.
Beyond these, there’s also optical imagery, a term for forensic-level satellite photography, such as from Digital Globe’s WorldView-3 satellite.
These images are expensive, but a superior way of identifying a specific target at an exact location.
“You can do some work by association,” says Kroodsma.
“Say you see a fleet of several hundred boats going somewhere on radar, then you look at the AIS and only you see 30 or 50, right? You can often infer from those what the other ones are doing. You have to be smart about it, but you can kind of piece it together from different sources of information – AIS or VMS, VIIRS, SAR and optical. Using those, you can put together the whole story about what's happening in a region.”
As they steamed west from the Galapagos, Bergman considered how many people they might encounter, densely packed together around one relatively small spot in the expanse of the ocean.
By night, the boat’s deck was now offering shelter for dozens of squid that, on approaching the surface, were disoriented by the lights on the Brigitte Bardot, and needed a resting place.
Then, one afternoon, the first vessel appeared on the radar, displaying the signal BZZ5K – a callsign not registered to any authorised vessel.
As it came into sight, Bergman noted a Chinese flag flying above the wheelhouse and what looked like a tattered black sail at the boat’s stern.
The hull was covered in rust and soot, obscuring any clear markings.
As they approached they could make out the name Hua Ying 819.
It was a squid jigger, and it was legal.
They ploughed on, disheartened but undeterred.
Waiting until nightfall, the captain Chris Holt manoeuvred the patrol vessel closer to the fleet.
Suddenly Bergman found himself on the edge of a city on the high seas, filled with white lights, but also vibrant greens and dim yellows.
Illuminated at night, these were the squid jiggers that Bergman and Aroni had seen on the VIIRS map.
They made their way through the fleet, trying to spot any suspicious activity, but their efforts were thwarted by limited satellite reception.
This meant that the AIS broadcasts of each vessel were unlikely to be reliable.
By then, Bergman and the crew were running out of time and fuel.
They decided to return to shore to consider their next move.
Bergman's trip hadn’t revealed any pirate boats, but maybe he could still find them – from back home in Peru.
And for that he was going to need the help of the Panamanian authorities.
Simon Ager
Sea Sheperd's interceptor vessel Brigitte Bardot on patrol
In March 2019, after Bergman’s intervention at the Waldorf Astoria, Panama agreed to make its daily VMS data public through GFW’s platform.
Bergman and the team were delighted.
“Even though it’s a small country, as far as the ocean is concerned, Panama has a huge presence because of the flag of convenience,” says Bergman.
He will now be able to re-examine the Chinese squid-jigger fleet's movements around the Galapagos in more detail, with the hope of identifying suspicious rendezvous – such as transshipments – at sea.
“This gives us another chunk of the fleet that we have really solid data on,” says Woods, who planned to make the Panama data publicly available in summer 2019.
Already, Indonesia and Peru have added their VMS data to the GFW map.
In May, Chile agreed to release its VMS data, making yet another 1,100 vessels publicly trackable.
Costa Rica has committed to doing the same in 2019, and GFW is now in discussions with Ecuador.
Currently, GFW employs around 30 experts in data analysis, machine learning, fisheries research and maritime surveillance, located around the globe.
As well as nurturing new projects and developing its machine learning capabilities, a large part of GFW’s focus is now on persuading governments to release their VMS data.
While continuing to work on locating specific targets, Bergman’s brief has also widened to GFW regional manager for Central and South America.
Much of this involves the sort of diplomacy on show in Panama, talking to government officials about the quid pro quo of having a more transparent fishing fleet.
“Once we know who is fishing and where, we’ll be one step closer to sustainably managing fisheries throughout the ocean,” says Kroodsma.
Though Bergman didn’t catch sight of any pirate squid fishers on the high seas, he’s had some success in tracking them down.
Late last year, shortly after his return from the South Pacific, a Chinese squid jigger, RUN DA 608, ducked inside Peru’s exclusive economic zone, which extends 200 nautical miles from its coast.
The authorities intercepted the vessel and found 19 tonnes of squid.
At that stage, Aroni set to work on retracing the vessel’s fishing track.
“The freshness of the squid didn’t match their purported fishing location”, says Bergman, “so we tracked the vessel in reverse and we identified a detour.” In the night, the vessel had slowed for three to four hours, presumably starting to fish in Peru’s waters.
“We had the vessel and the fish seized,” he says.
“Before GFW, we did not have the data to do this.”
The team hopes that within a decade, all VMS data will be public, and that improved satellite coverage of the world's oceans – thanks to companies such as Planet Labs, which now has 170 miniature satellites in orbit – will bring more frequent and more reliable AIS detections.
“The constellations that are going up right now will cover the whole ocean for the first time.
Using different technologies, we'll really have the possibility of detecting all these vessels,” says Woods.
“It’s more cost-effective than wandering around a big chunk of the ocean and hoping to run into something. And it’s much more targeted.”
Bergman agrees: “Once we can monitor the dark fleet, the crime that's happening in the ocean will be pushed out into the open. They'll have nowhere to hide.”
Links :