- Forbes : Volvo Ocean Race: A $20 Million Test Of Sailing Endurance
Saturday, August 9, 2014
Join the adventure of a lifetime | Volvo Ocean Race 2014-15
Friday, August 8, 2014
Pollution triples mercury levels in ocean surface waters, study finds
There's a tight and surprising link between the ocean's health and ours, says marine biologist Stephen Palumbi.
He shows how toxins at the bottom of the ocean food chain find their way into our bodies, with a shocking story of toxic contamination from a Japanese fish market.
His work points a way forward for saving the oceans' health -- and humanity's.
Toxic metal threatens marine life as it accumulates faster in shallow layers than in deep sea due to human activity
Mercury is accumulating in the surface layers of the seas faster than in the deep ocean, as we pour the element into the atmosphere and seas from a variety of sources, including mines, coal-fired power plants and sewage.
Mercury is toxic to humans and marine life, and accumulates in our bodies over time as we are exposed to sources of it.
Since the industrial revolution, we have tripled the mercury content of shallow ocean layers, according to the letter published in the peer-review journal Nature on Thursday.
Mercury can be widely dispersed across the globe when it is deposited in water and the air, the authors said, so even parts of the globe remote from industrial sources can quickly suffer elevated levels of the toxic material.
For several years, scientists have warned that pregnant women and small children should limit their consumption of certain fish, including swordfish and king mackerel, because toxic metals including mercury and lead have been accumulating in these species to a degree that made their over-consumption dangerous to human health.
Pregnant women are particularly at risk because the metals can accumulate in the growing foetus, and in sufficient quantities can cause serious developmental disorders.
The scientists behind Thursday’s letter to Nature, including researchers from the prestigious Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution in the US, stopped short of warning on the dangers to human health from our pouring of mercury into the oceans.
However, they said, further research could yield more advice on the potential impacts: “This information may aid our understanding of the processes and the depths at which inorganic mercury species are converted into toxic methyl mercury and subsequently bioaccumulated in marine food webs.”
Simon Boxall, lecturer on ocean and Earth science at the University of Southampton, said it was “hard to say” from the research how much damage had already been done to marine life, including edible fish species, and how quickly any such damage would become apparent.
“I would not stop eating ocean fish as a result of this,” he said.
“But it is a good indicator of how much impact we are having on the marine environment. It is an alarm call for the future.
Deep waters in the North Atlantic showed more mercury content than similarly deep waters of the South Atlantic and the Southern and Pacific Oceans, the authors of the report said.
Mercury at the surface will disperse to lower layers in time, but this can take decades.
However, the process of the damage to marine life becoming apparent can be faster in some areas, such as those closer to the poles, than areas nearer the equator, said Dr Boxall.
The north pole and the Arctic circle, because of the winds and ocean currents, is an area where many pollutants released elsewhere across the globe accumulate: top predators such as polar bears have been found to have high levels of toxins in their bodies as a result.
These animals are sometimes eaten by indigenous Arctic peoples.
“In the Arctic and Antarctic, you will be starting to see some of this now,” he said.
“But with deep-sea fishing in the tropics you will not see it yet, but you will see it within a hundred years.”
Mercury emissions from coal-fired power plants can be reduced by using chemical filters, but while this is increasingly the norm in the rich world many developing countries have yet to catch up. Another source of the metal is from sewage.
Developed countries have means to reduce this impact, but again developing countries are less likely to have in place the treatment systems necessary.
Links :
- CBS : Oceans tainted with more man-made mercury
- Zero Mercury Working Group
Thursday, August 7, 2014
Australia AHS update in the Marine GeoGarage
3 charts have been added and 16 charts have been updated in the Marine GeoGarage
(AHS update 08/07/2014)
- Aus144 Australia South Coast - Victoria - The Rip
- Aus155 Australia South Coast - Victoria - Approaches to Port of Melbourne
- Aus81 Australia West Coast - Western Australia - Approaches to Geraldton
- Aus546 Papua New Guinea - New Britain North Coast - Cape Lambert to Bangula Bay
- Aus547 Papua New Guinea - New Britain North Coast - Bangula Bay to Eleonora Bay
- Aus242 Australia East Coast - Queensland - Port Bundaberg including Burnett River
- Aus647 Papua New Guinea - South Coast - Approaches to Caution Bay NEW
- Aus648 Papua New Guinea - South Coast - Caution Bay NEW
- Aus54 Australia North West Coast - Western Australia - Port Hedland
- Aus181 Australia South Coast - Victoria - Corner Inlet
- Aus182 Australia South Coast - Plans in Victoria - South East Coast
- Aus63 Australia North West Coast - Western Australia - Mary Anne Passage
- Aus700 Australia North Coast - Queensland - Western Approaches to Torres Strait
- Aus637 Papua New Guinea - North East Coast - Trobriand Islands NEW
- Aus56 Australia North West Coast - Western Australia - Port Walcott
- Aus606 Indian Ocean - Approaches to Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Aus607 Indian Ocean - Cocos (Keeling) Islands South Keeling
- Aus237 Australia East Coast - Queensland - Brisbane River - The Bar to Lytton Reach
- Aus802 Australia South Coast - Victoria - Cape Liptrap to Cliffy Island
Note : AHS updates their nautical charts with corrections published in:
ShoreZone, public access to a coastal map : Uses for spill planning tool expands
Learn how to access millions of coastal aerial photos right from your desktop using the ShoreZone Alaska Flex Site.
From Washington Times by Molly Dischner
A program originally brought to Alaska to support oil spill planning and response efforts in Cook Inlet has since expanded to most of the state with uses from coastal monitoring to art and education.
The coastal mapping endeavor ShoreZone’s Alaska debut was as a Cook Inlet Regional Citizens Advisory Council pilot project in 2001. Now, about 80 percent of Alaska’s coastline is mapped including Southeast Alaska and the North Slope.
“Having the biology and the geology together is a robust data set,” said ShoreZone’s Darren Stewart, who works for The Nature Conservancy as a coordinator among the various partners.
In addition to oil and gas uses, the database is valuable for Coast Guard search and rescue operations, researchers doing reconnaissance and selecting sites, marine debris cleanup efforts, and recreation planning such as planning kayak trips and looking for safe landing spots for boats, Stewart said.
“Being able to see an area before you get there saves a lot of time and money and resources,” Stewart said.
This summer, the National Marine Fisheries Service is funding the next step in mapping Alaska’s coast - about 2,500 miles along the Yukon-Kuskokwim Delta shoreline from Cape Newenham to Emmonak, including Nunivak Island.
That work will be done in two surveys in July and August, and cost about $300,000.
NMFS is the primary funder this summer, but the Yukon Delta National Wildlife Refuge will provide various services like fuel drops, lodging and other logistics support, Stewart said.
A private contractor, Coastal and Ocean Resources Inc., or CORI, collects the data that feeds into the maps. A biologist and a geomorphologist will ride in a helicopter along the coast, taking video and shooting still images, and narrating along the way.
Generally, the team will follow the same standardized protocol that has been used throughout the state - including doing the work when there are the lowest tides and the most light.
“They want the entire coastline from the lowest of the low waterline to the supertidal zone,” Stewart said.(backslash)
In some places, additional information is collected based on interest - for instance, a baseline hydrocarbon study was done on the Nort Slope.
Later on, mappers will listen to the narration and use the imagery to create maps in units.
That can take several months, and depends on funding, Stewart said.
Eventually, the database that’s built allows for queries about a variety of things - where logs are likely accumulate, whether a stretch of coast has pebble or boulders or a sandy beach, and the habitat there, said CORI’s John Harper, who has been involved with the project since it started in British Columbia.
CORI has done all but one of the surveys in Alaska, according to Stewart, and funding has come from a variety of partners - about 30 to 40 organizations have been involved at one time or another.
“It’s very cool that we’ve had this array of funding,” Harper said.
Rooted in spill response and planning
ShoreZone has its roots in oil spill planning - the program started in British Columbia for that purpose, and first came to Alaska for the same.
Cook Inlet Regional Citizens Advisory Council Director of Science and Research Sue Saupe said several organizations recognized the need for more information about Alaska’s coast after the Exxon Valdez oil spill.(backslash)
In 2001, the Cook Inlet advisory council, or CIRCAC, decided to see if ShoreZone could fill that need and funded the first pilot project.
“We wanted a better inventory of all the coastlines in Cook Inlet,” she said.
The early goal was to provide habitat information and imagery that could be used in emergency situations.
The more information that is available about the coast, the easier it is to plan for a spill and cleanup, and minimize the impacts, because different habitats and landscape types respond differently to various treatments, she said.
For instance - oil will linger longer on a slat marsh than an exposed stretch of rocks.
ShoreZone provided the information that CIRCAC wanted, so after the pilot, the group started approaching other potential partners around the state to get involved.
Within three years, all of Cook Inlet, the outer Kenai Peninsula coast, the Katmai region and northern portion of Kodiak were mapped.
“I think the imagery is what really sparked people’s interest in making that happen,” Saupe said.
Eventually, the project expanded to Southeast Alaska, and then Bristol Bay and most recently the North Slope in 2012 and St. Lawrence Island in 2013, Stewart said.
The uses within the oil and gas realm are varied, Saupe said.
“This imagery has so much value, I think, in oil spill planning and response,” Saupe said.
Saupe said the program helps an oil spill response team on several levels - operations, planning and logistics.
During the 2012 Kulluk incident when the Shell drill rig separated from its tow and went aground in a storm near Kodiak, Harper said the response team relied on ShoreZone to figure out where to land, where to store booms and how to prepare for grounding and minimizing damages.
Flying the coast
Today, the ShoreZone website is accessible to anyone with a computer and fast enough internet connection.
Log on, and you can fly all the segments of Alaska’s coast that are mapped.
But it didn’t start that way.
Early on, the ShoreZone partners had to figure out how to make the data available, as the database deliverable was simply a disc of information, imagery and maps, Saupe said.
In 2004, the National Marine Fisheries Service agreed to host the data and make sure it was seamless throughout the various regions of the data, and in 2005 the agency released the first integrated website, making all the data collected so far available to the public.
The website is always being improved, Saupe said.
“It’s just a constant effort, constant effort by NOAA to keep upgrading, take advantage of new tools,” she said.
More recently, the video displayed on the website went from one second capture to full streaming video for certain portions of the database.
Saupe said the partnership is always looking for ways to improve access and use of ShoreZone in oil spill planning and response, and in other capacities.
One of the efforts has been to create offline tools, so that responders in areas with limited internet access can still use the ShoreZone information.
An early iteration of that effort is available by borrowing a hard drive and pulling all the data from it, but that’s a cumbersome process.
Another version is in the works, which would allow users to pull the data right from the internet onto a local drive.
For now, however, Saupe said the website remains the best way to access the data.
CIRCAC has also worked with the Alaska Oceans Observing System, or AOOS, on a program that integrates ShoreZone data with other information responders might want, Saupe said.
The Cook Inlet Response Tool includes more than 100 data layers, such as ShoreZone habitat information and video, realtime weather sensors and webcams, oil persistence, and marine mammal information.
Saupe said it was a “powerful way to look at information.”
AOOS also has ShoreZone data merged with additional databases for other regions of the state, including the Gulf of Alaska, Prince William Sound and the Arctic.
“The goal was to take this ShoreZone imagery the next step,” Saupe said.
CIRT also includes Geographic Response Strategies, which are pre-planned, site-specific protection measures for anadramous streams, archeological sites and other places considered fragile or in need of protection.
Those were commissioned by Alaska’s Department of Environmental Conservation, and are available throughout the state, although they - like ShoreZone - began in Cook Inlet.
Other patches remain to be mapped, including Norton Sound and parts of the Aleutian Islands, in part because it’s difficult to find funding for those areas.
Other gaps in the data are the Southwest Alaska Peninsula, including King Cove and Sand Point, which are imaged but not mapped, Glacier Bay, the Pribilof Islands and Unimak Pass.
The western Aleutians will be particularly difficult, and may have to be done by boat, Stewart said.
“Even though its logistically challenging space, getting the Aleutians done is really important,” Stewart said.
Harper said that Unimak Pass is a priority because of the shipping traffic in the region.
“Even just regular cargo ships, they carry huge amounts of oil onboard,” Harper said.
For now, there’s no set plan for updating the information as the coastline changes, although the mapping protocol relies on small homogenous units, so updates could be done piece-by-piece if necessary.
Saupe said that the Cook Inlet was already reflown in 2009, as technology improved and the original imagery became outdated.
The imagery statewide is also useful for gauging change, she said.
“That imagery has become a very important data source in and of itself,” she said.
Beyond oil and gas
The survey process itself also leads to other interesting discoveries, Saupe said.
For instance, during the Gulf of Alaska mapping, researchers discovered that macrocystis kelp beds previously thought not to extend past Icy Strait are actually found in the western Gulf of Alaska.
After a small bed in Kenai and a larger bed in Kodiak were noted, CIRCAC funded dive studies to learn more about the habitat, Saupe said, and researchers have looked through historical records to try to learn more about its range, and if this is a change.
CIRCAC has also used the habitat information from ShoreZone to develop further studies of salt marshes in Cook Inlet, she said.
ShoreZone has also been used to develop two art exhibits, which pair large prints of the photos taken during the survey with scientific information about each area.
The exhibits looked at the Gulf of Alaska and the Arctic, and have been installed in various places throughout the state, including the State Museum in Juneau.
Communities also use ShoreZone for coastal planning, Stewart said.
“Just to get a good bird’s eye view of what’s there on the coast,” he said.
ShoreZone is also a tool for education, Saupe said, both in schools and communities.
Saupe demonstrated the website in Kodiak.
She had a young girl spot the place where she had taken a long beach walk, and a woman point out important archaeological sites around the island.
A U.S. Coast Guard member responsible for pulling information when preparing for rescues said it would help with that work in the future.
“Right there, you just had all these different levels of interest,” Saupe said.
The website is also being used in some schools, both to learn about the coast and as the basis for other projects.
One projects has students using the imagery to collect history and information about the villages and surrounding areas from local elders, Saupe said.
Wednesday, August 6, 2014
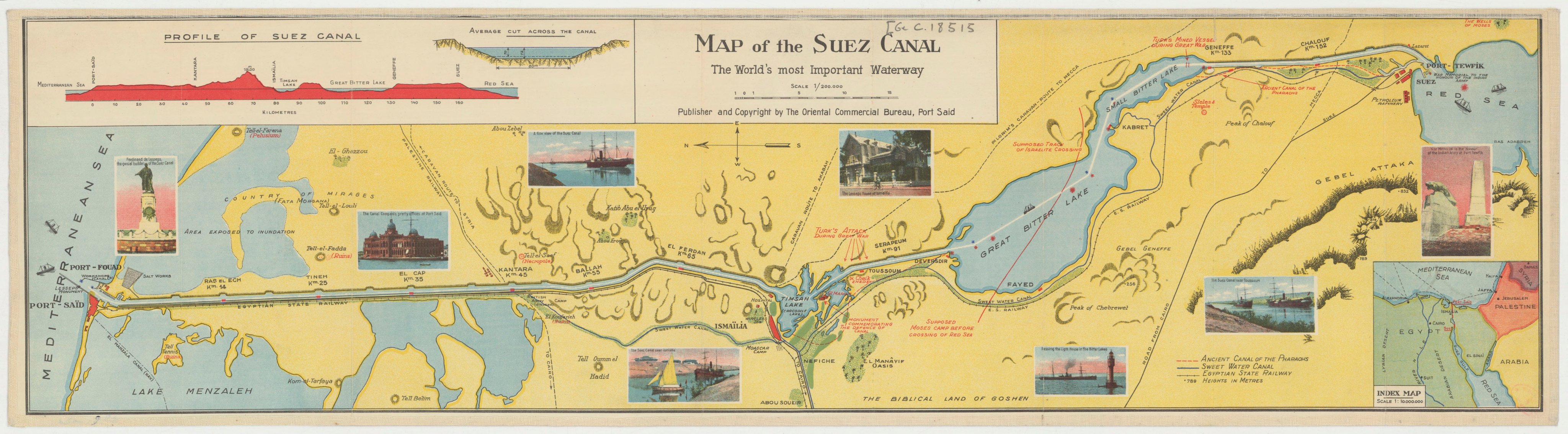
Egypt to build new Suez canal
From The Guardian by Patrick Kingsley
Egypt plans to add an extra lane to the Suez canal, one of the world's most important thoroughfares for trade, in an attempt to increase the number of ships using it each day.
The canal, which allows ships to travel from Europe to Asia without passing southern Africa,
only provides for one-way traffic, with occasional room for ships to
pass each other.
A new 45-mile lane, plans for which were announced on
Tuesday by Egypt's president, Abdel Fatah al-Sisi, would allow ships to
travel in both directions for just under half of the canal's 101 miles.
"This
giant project will be the creation of a new Suez canal parallel to the
current channel," said Mohab Mamish, the chairman of the Suez Canal
Authority, in a televised speech.
According to Egypt's main state
news website, Mamish hopes the new channel will be working within a
year, but such a quick turnaround is by no means certain.
It is also
unclear to what extent the expansion would speed up the canal's
operations, said Angus Blair, a Cairo-based analyst who has followed the
project's development.
"They are only increasing capacity in a part of the canal, so the
merits of it still have to be weighed up," said Blair, the president of
the Signet Institute, an economic and political thinktank.
"They are
essentially turning a single carriageway into a motorway halfway
through."
In a speech to the nation on Tuesday, Sisi said the
project would receive no financing from abroad, and that he hoped its
$4bn (£2.4bn) cost would instead be offset by independent contributions
from individual Egyptians.
"We want all Egyptians to hold shares in this
project," he said.
Once its cost had been recouped, it was hoped
the project would provide lasting stability to Egypt's ailing economy,
Sisi said.
Revenues from the Suez canal, which total about $5bn (£3bn)
every year, are a crucial source of foreign currency for the Egyptian economy, which has been battered by three years of political instability that have ruined the country's tourism industry and frightened away western investors.
The Suez canal is of great symbolic as well as economic importance to Egypt.
Opened 145 years ago, it remained under colonial control until 1956, when Egypt's then president, Gamal Abdel Nasser, wrested it into Egyptian ownership in an episode that remains a source of deep national pride.
Links :
- GeoGarage blog : Suez canal transit in 30 seconds
Tuesday, August 5, 2014
‘The man who doesn’t breathe’: World-record diver can hold his breath underwater for 22 minutes
a Guinness World Record.
He believes that controlling our breath means controlling our lives.
From DailyMail
- Stig Severinsen is the holder of multiple records in diving using his 'State of Zen' technique to control his breathing
- Also swam 500ft underwater in 2mins and 11secs
- Mr Severinsen, 41 from Aalborg, began free diving in 2003
- By the end of first year of practising he had already broken three records
He also holds the record for the longest underwater swim, travelling 500ft (152m 40cm) in just two minutes and 11 seconds.
Monday, August 4, 2014
Every reported shark attack, worldwide, since 1580
REMUS SharkCam: The hunter and the hunted from Woods Hole Oceanographic Inst.
From io9
The map is here. And for a fun take on the data, check out David Shiffman's awesome article (and my source for the map): "24 species of shark that have killed fewer people than Jack Bauer on 24".